“Mangrove forests, like in the Everglades, serve as spawning grounds and nurseries for fish and as habitat for a wide array of organisms. But salt marshes are also ecologically valuable.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
“Mangrove forests, like in the Everglades, serve as spawning grounds and nurseries for fish and as habitat for a wide array of organisms. But salt marshes are also ecologically valuable.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
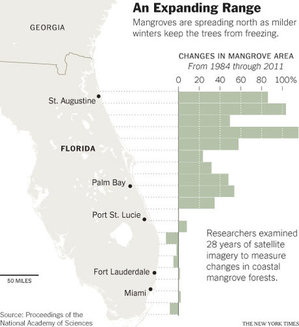
(p. A14) Much of the Florida shoreline was once too cold for the tropical trees called mangroves, but the plants are now spreading northward at a rapid clip, scientists reported Monday [December 30, 2013]. That finding is the latest indication that global warming, though still in its early stages, is already leading to ecological changes so large they can be seen from space.
. . .
The mangrove forests that fringe shorelines in the tropics are among the earth’s environmental treasures, serving as spawning grounds and nurseries for fish and as habitat for a wide array of organisms. Yet in many places, mangroves are critically endangered by shoreline development and other human activities.
So a climatic change that allows mangroves to thrive in new areas might well be seen as a happy development.
. . .
For years, scientists working in Florida had been noticing that mangroves seemed to be creeping northward along the coast. The new study is the first to offer a precise quantification of the change, using imagery from a satellite called Landsat, and to link it to shifts in the climate.
Patrick Gillespie, a spokesman for Florida’s Department of Environmental Protection, offered no specific comment on the new paper. By email, he said the agency had indeed “seen an increase in mangrove habitats to the north and inward along the Atlantic coast. It’s difficult to determine whether this is good or bad for the ecosystem because it’s happened over a relatively short period (p. A16) of time and may be a result of many factors.”
For the full story, see:
JUSTIN GILLIS. “Spared Winter Freeze, Florida’s Mangroves Are Marching North.” The New York Times (Tues., December 31, 2013): A14 & A16.
(Note: ellipses, and bracketed date, added.)
(Note: the online version of the story has the date December 30, 2013.)
The academic article on Florida’s thriving mangrove forests, is:
Cavanaugh, Kyle C., James R. Kellner, Alexander J. Forde, Daniel S. Gruner, John D. Parker, Wilfrid Rodriguez, and Ilka C. Feller. “Poleward Expansion of Mangroves Is a Threshold Response to Decreased Frequency of Extreme Cold Events.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) 111, no. 2 (January 14, 2014): 723-27.
Source of Florida map graphic: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.