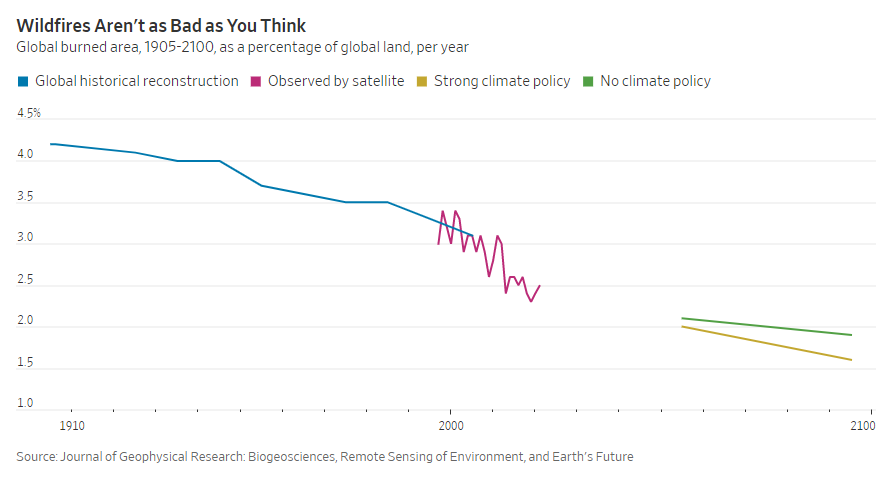
(p. A19) In the early 1900s, about 4.2% of land world-wide burned every year, as you can see on the nearby graph. A century later, that had dropped almost to 3%. That decline has continued through the satellite era, and 2021 is likely to end with only 2.5% of the globe having caught fire, based on data through Aug. 31 [2021].
This data is entirely noncontroversial. Even a report from the World Wildlife Fund—chillingly subtitled “a crisis raging out of control?”—concedes midway through that “the area of land burned globally has actually been steadily declining since it started to be recorded in 1900.”
Human ingenuity gets the credit: People have moved from hearths to power stations, converted untamed land into protected farms, and created enough excess wealth that societies can increasingly afford to defend our surroundings with fire suppression and forest management.
. . .
It is true that more people will probably be threatened by fires in the future, but this is because part of the world’s growing population will settle where wildfires are more common. The number of homes in high-fire-risk zones in the Western U.S. has increased 13-fold over the past 80 years and is set to increase further by 2050. A 2016 Nature study concludes this is true globally. “Contrary to common perception,” the researchers write, “human exposure to wildfires increases in the future mainly owing to projected population growth in areas with frequent wildfires, rather than by a general increase in burned area.”
For the full commentary, see:
(Note: ellipsis, and bracketed year, added.)
(Note: the online version of the commentary has the date October 27, 2021, and has the same title as the print version.)
Lomborg’s quotation from he report of the World Wildlife Fund is from p. 8 of:
The Nature study Lomborg quotes above is:

