 Source of graph: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
Source of graph: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
(p. A13) Sclerotic growth is America’s overriding economic problem. From 1950 to 2000, the U.S. economy grew at an average rate of 3.5% annually. Since 2000, it has grown at half that rate–1.76%. Even in the years since the bottom of the great recession in 2009, which should have been a time of fast catch-up growth, the economy has only grown at 2%.
. . .
. . . the U.S. economy is simply overrun by an out-of-control and increasingly politicized regulatory state. If it takes years to get the permits to start projects and mountains of paper to hire people, if every step risks a new criminal investigation, people don’t invest, hire or innovate.
. . .
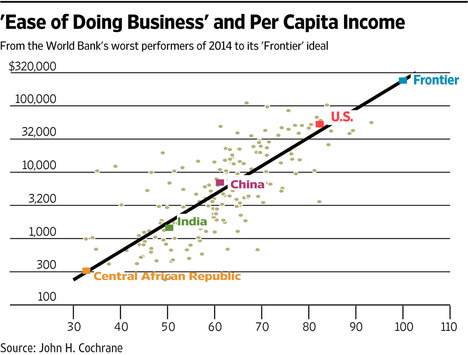
How much more growth is really possible from better policies? To get an idea, see the nearby chart plotting 2014 income per capita for 189 countries against the World Bank’s “Distance to Frontier” ease-of-doing-business measure for the same year. The measure combines individual indicators, including starting a business, dealing with construction permits, protecting minority investors, paying taxes and trading across borders.
. . .
Most of all, the country needs a dramatic legal and regulatory simplification, restoring the rule of law. Middle-aged America is living in a hoarder’s house of a legal system. State and local impediments such as occupational licensing and zoning are also part of the problem.
. . .
There is hope. Washington lawmakers need to bring about a grand bargain, moving the debate from “they’re getting their special deal, I want mine,” to “I’m losing my special deal, so they’d better lose theirs too.”
For the full commentary, see:
JOHN H. COCHRANE. “Ending America’s Slow-Growth Tailspin; The U.S. economy needs a dramatic legal and regulatory simplification.” The Wall Street Journal (Tues., May 3, 2016): A13.
(Note: ellipses added.)
(Note: the online version of the commentary has the date May 2, 2016.)

