“Work has been put on hold for this stretch of 132nd Street between Blondo Street and West Maple Road. Omaha officials say the stimulus funds will be worth the wait, but some nearby residents are upset about the slowdown.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the Omaha World-Herald article quoted and cited below.
“Work has been put on hold for this stretch of 132nd Street between Blondo Street and West Maple Road. Omaha officials say the stimulus funds will be worth the wait, but some nearby residents are upset about the slowdown.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the Omaha World-Herald article quoted and cited below.
We live near the still-two-lane stretch of 132nd pictured above, and were happy to read in the Omaha World-Herald early last spring that the city would be finishing the widening of 132nd, by widening the above stretch during the summer of 2009. As the summer progressed and widening did not, we became more and more puzzled.
Well, after you read the passages quoted below, you will ‘know the rest of the story’ as Paul Harvey used to say:
(p. 1A) The federal stimulus program, which was designed to accelerate roads projects around the country, instead put the brakes on widening a major Omaha thoroughfare.
The chance to grab $3.5 million in stimulus funds was worth delaying a widening project along 132nd Street between West Maple Road and Blondo Street, Omaha officials decided.
Work was supposed to begin last summer. Now the project between the Champions and Eagle Run golf courses won’t begin until next spring.
Preliminary work was begun in March, when utility lines were moved out of the way. Part of the street was closed for that work.
Area residents expected more crews to start work during the summer.
When nothing happened for months, a handful of residents in the nearby Sunridge neighborhood called the city. They com-(p. A2)plained that digging from the utility work was causing mud and rainwater to pool near the subdivision’s entrances off 132nd Street.
Resident Mary Ellen Pollard was surprised to find out that the widening work had been put on hold because of the stimulus program.
“I thought that stimulus package was for projects that were ready to go,” she said Monday. “If it was ready to go, why didn’t they proceed with it? . . . The barricades are up. Let’s go get it done.”
Plans change, public works officials said.
Meeting federal stimulus guidelines for environmental studies on the 132nd Street project, plus other planning and documentation requirements, took several months, City Engineer Charlie Krajicek said.
“We expected to have some work going this year, but it just didn’t work out,” he said.
For the full story, see:
Tom Shaw. “Stimulus slows 132nd St. work.” Omaha World-Herald (Tuesday October 6, 2009): 1A-2A.
(Note: the online version of the article is dated Weds., October 7 and has the slightly expanded title: “Stimulus Watch: Program slows 132nd St. work.”)
(Note: ellipsis in original.)
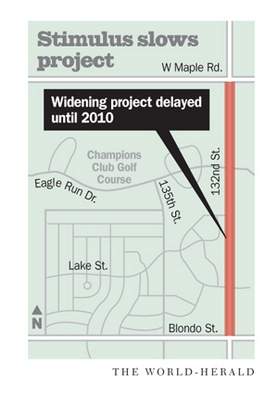
Source of map: online version of the Omaha World-Herald article quoted and cited above.