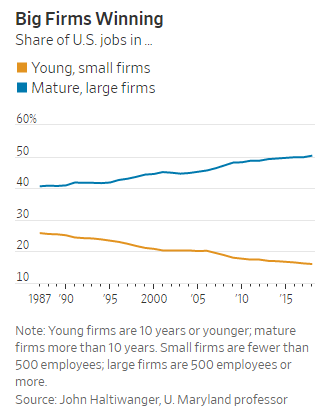
(p. 1) A key scientific breakthrough that would eventually help protect millions from Covid-19 began with a chance meeting at a photocopier — in 1997, between Professor Katalin Kariko and Dr. Drew Weissman, whose work laid the foundation for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines.
It’s exactly the type of story that has executives itching to get people back to offices. Chance meetings like this are essential for innovation, the theory goes. “Remote work virtually eliminates spontaneous learning and creativity because you don’t run into people at the coffee machine,” Jamie Dimon, the chief executive of JPMorgan Chase, recently told shareholders.
Creativity is hard to quantify. But research, including studies of companies working remotely during the pandemic, supports Mr. Dimon’s argument only up to a point. The data shows that in-office work is helpful at one part of the creative process: forming initial relationships, particularly with people outside your normal sphere.
. . .
(p. 5) A new analysis of announcements by the 50 largest public video game companies, by Ben Waber and Zanele Munyikwa, found that companies that moved to remote work during the pandemic had more delays in new products than before the pandemic, while those that worked in person did not.
The researchers have a hypothesis about why. They also tracked billions of communications — email, chat and calendar data — among information employees at a dozen large global companies over recent years. They found that while working remotely, individual workers were more productive than before, and communicated more with people at different levels of the company and with close colleagues. But they communicated 21 percent less with their weak ties. Perhaps the video game developers lost the benefit of asking a co-worker from a different department to test a prototype, for example, or of running into someone from marketing and brainstorming ideas for selling a new game.
“I do think eventually technology will help here, but the stuff that’s widely available today just doesn’t do it,” said Mr. Waber, co-founder of Humanyze, a workplace analytics company started at M.I.T. Media Lab, where he got a Ph.D. “It probably would be fine if those initial water cooler conversations happened remotely. It’s just less likely they would.”
. . .
Another study, using location tracking technology to follow scientists and engineers at a global manufacturing firm, found that people who often walked by one another in the office, like on their way to the printer or the restroom, were significantly more likely to end up collaborating, especially at the beginning of projects.
“For most collaboration, takeoff is the most challenging bit, and that’s when we find co-location is most helpful,” said Felichism W. Kabo, a research scientist at the University of Michigan and the study’s author. “When people have a prior relationship, it’s much easier to sustain that virtually.”
. . .
For Professor Kariko, there was a long period when it seemed that her research on messenger RNA would never get funding. It was so different from that of her close colleagues, she has said, that it had little support. It took that encounter at the copy machine — meeting Dr. Weissman, who brought a different perspective and a desire to make a vaccine — to change that.
For the full commentary, see:
(Note: ellipses added.)
(Note: the online version of the commentary was updated Sept. 4, 2021, and has the title “When Chance Encounters at the Water Cooler Are Most Useful.”)
The article by Waber and Munyikwa mentioned above is:
The article by Kabo mentioned above is: