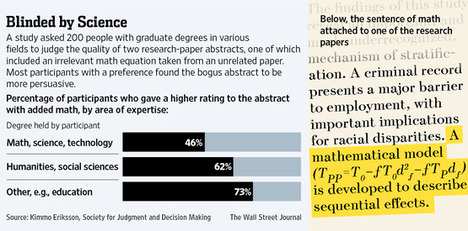
(p. C7) In chronicling the decline and fall of the Roman Empire, Edward Gibbon declared that “if a man were called to fix the period in the history of the world during which the human race was most happy and prosperous, he would, without hesitation, name that which elapsed from the death of Domitian to the accession of Commodus.” Gibbon himself elegantly narrated how happiness and prosperity withered after this flowering between 96 and 180 A.D. But what about the near-millennium of Roman history that came before? “What was it,” as Anthony Everitt asks in “The Rise of Rome,” “that enabled a small Italian market town by a ford on the river Tiber to conquer the known world” and thereby made Gibbon’s golden years possible?
. . .
Most of that economic activity, whether it developed autonomously as a result of lower costs or was driven by the coercive rule of the state, was catalyzed by the Mediterranean, with which even the sophisticated Roman road network could not compete. Yet in the period from the middle of the third century B.C. to the middle of the first, Mr. Everitt, following his literary sources, directs our attention to Hamilcar, the Carthaginian general; and to Hannibal, his hot-tempered son, leading elephants first across the Pyrenees and then the Alps. Both are important, and, had they not been defeated, Rome would have had a very short “rise” indeed. But the real action was on the Mediterranean. As the number of shipwrecks datable to these years attests, it was being crossed by trading vessels with a frequency never yet seen and never again matched–including the halcyon years hymned by Gibbon.
Sometimes the data can preserve an astonishingly precise record of a trade route. For example, storage containers–probably for wine–salvaged from the spectacular wrecks at Grand Congloué, off Marseilles, bear the stamp “SES.” Archaeologists have confidently linked this mark with a certain Sestius, who must have manufactured the wares at the villa we know he owned in southwestern Tuscany, no mean distance away.
When the shipwreck data, which suggest increased economic activity, are considered alongside the population contraction that Rome suffered in its bloody military campaigns, a tentative but rich answer to Mr. Everitt’s question begins to emerge: Rome’s rise is a story of economic growth, not divine intervention or native virtue. And although even this account, like all our conclusions about the distant past, must be provisional, it is at least anchored in an empirical model of how income gains from trade and lowered transaction costs were not swallowed up by an ever-expanding population.
For the full review, see:
BRENDAN BOYLE. “BOOKSHELF; The Economy of Empire; The rise of the world’s greatest empire is as much a story of shipping and markets as of divine providence and individual virtue.” The Wall Street Journal (Sat., September 22, 2012): C7.
(Note: ellipsis added.)
(Note: the online version of the article was dated September 21, 2012.)