Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
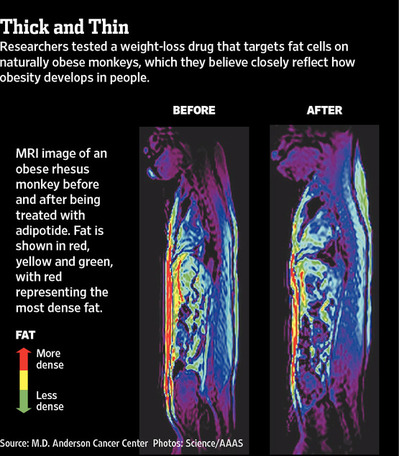
(p. A6) A drug that kills a type of fat cell by choking off its blood supply caused significant weight loss in obese monkeys, potentially setting the stage for a new pharmaceutical approach to attacking obesity, according to a study released Wednesday.
After four weeks of treatment, obese monkeys given daily injections of the drug, called adipotide, lost an average of 11% of their body weight. They also had big reductions in waist circumference and body-mass index and, importantly, striking improvement in their ability to process insulin, researchers said. The drug had no effect on weight when given to lean monkeys.
Results of the study, performed at M.D. Anderson Cancer Center in Houston and published online by the journal Science Translational Medicine, confirmed a 2004 report from the same research team showing marked weight loss in mice treated with the agent.
. . .
The researchers’ 2004 paper showing a 30% weight loss in obese mice drew skepticism. Randy J. Seeley, director of the diabetes and obesity center at the University of Cincinnati, figured destroying white fat cells would make animals–and people–sick. But his own lab eventually replicated the mouse study, using rats instead, and now he is intrigued.
“This is really new stuff,” Dr. Seeley said of the latest results. “There’s no way to know if this will become a therapy or not, but at least it opens up a new way to think about therapies, and we have not had a lot of those.” He isn’t involved with the research.
For the full story, see:
RON WINSLOW. “Drug Offers Hope in Obesity Fight; Treatment Targeting Fat Cells Caused Significant Weight Loss in Monkeys; Human Trials to Begin Soon.” The Wall Street Journal (Thurs., November 10, 2011): A6.
(Note: ellipsis added.)
(Note: the last two sentences quoted above appeared in the online, but not the print, version of the article.)
 “One of the monkeys used in the study. Obese monkeys lost an average of 11% of their body weight after four weeks of treatment.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited above.
“One of the monkeys used in the study. Obese monkeys lost an average of 11% of their body weight after four weeks of treatment.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited above.