Source of Image: NYT commentary cited below.
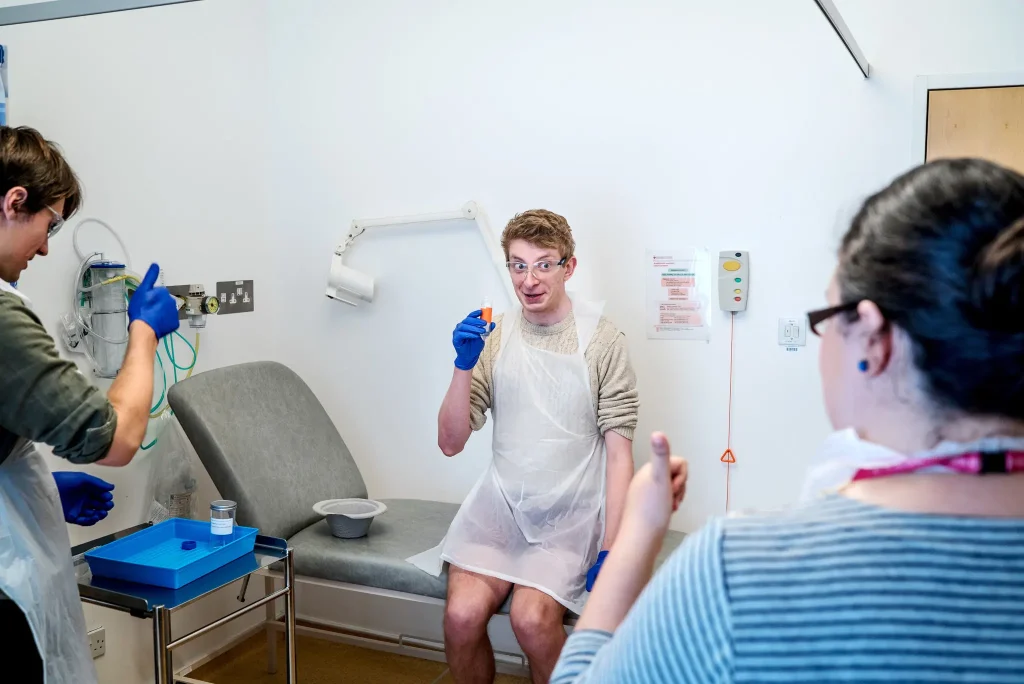
(p. D3) “I was curious.” That’s how James M. Duggan, an Oxford University medical student, explains why he agreed to swallow a big dose of live typhoid bacteria.
. . .
Mr. Duggan, 33, was not on a self-destructive sympathy bender. Like more than 100 other residents of Oxford, England, he was taking part in a trial of a new typhoid vaccine.
Typhoid fever, caused by the bacteria Salmonella typhi and spread in food and water, kills almost 200,000 victims a year — many of them young children — in Africa, Asia and Latin America. Survivors may suffer perforated intestines, heart problems and other complications.
The experimental vaccine was a big success. The trial’s results were published in The Lancet on Thursday [Sept. 28, 2017]: the vaccine turned out to be 87 percent effective.
. . .
“These are great results,” said Dr. Anita Zaidi, the foundation’s director of diarrheal diseases. “And challenge tests are a great way to short-circuit the process of proving it works.
“If we’d done this in the field, we would have had to follow children for three or four years.”
So-called challenge tests involve giving subjects an experimental vaccine and then deliberately infecting them with the disease to see if it protects them.
These tests can only be done with illnesses — like cholera or malaria — that can be rapidly and completely cured, or with diseases — like seasonal flu — that normally do not damage healthy adults.
. . .
So what would motivate dozens of well-educated Britons to swallow a vial full of the germs that made Typhoid Mary famous? In interviews, they gave various reasons.
Some, like Mr. Duggan, were curious. Some wanted to help poor people. And some mostly wanted the cash.
Participants who followed all the steps, which included recording their temperatures online, making daily clinic visits and providing regular blood and stool samples, received about $4,000.
They all said they understood the risks.
For the full commentary see:
(Note: ellipses, and bracketed date, added.)
(Note: the online version of the commentary has the date Sept. 28, 2017, and has the title “They Swallowed Live Typhoid Bacteria — On Purpose.”)
The print version of The Lancet article mentioned above is:

