 George B. Kaiser. Source of photo: http://www.forbes.com/finance/lists/10/2003/LIR.jhtml?passListId=10&passYear=2003&passListType=Person&uniqueId=OXNB&datatype=Person
George B. Kaiser. Source of photo: http://www.forbes.com/finance/lists/10/2003/LIR.jhtml?passListId=10&passYear=2003&passListType=Person&uniqueId=OXNB&datatype=Person
(p. A1) In 2002, Kathleen Eisbrenner, then an executive at El Paso Corp., spent months trying in vain to find a buyer for the company’s novel technology for importing natural gas.
In February 2003, she left for a vacation in Cancun, convinced that El Paso would be forced to abandon the project. As she sat on the beach one afternoon, she got a call on her cellphone. A colleague had a message from an intermediary, who said he had an "interested buyer," identified only as a "Midwest billionaire."
"It’s Warren Buffett calling," she recalls telling her husband as they clinked pina colada glasses together in celebration. "I was absolutely sure."
But it wasn’t Mr. Buffett. It was another billionaire named George B. Kaiser.
. . .
(p. A6) . . . , Ms. Eisbrenner called Nicolas Saverys, the chief executive of Belgium-based Exmar NV. Exmar was building two of the new-style LNG vessels. Ms. Eisbrenner gushed that there was a wealthy buyer. Mr. Saverys was initially skeptical. He changed his mind in late February 2003 after meeting Mr. Kaiser in New York. "At last, I was talking to someone who was putting his own money at stake," he says.
Mr. Saverys sealed the relationship by presenting Mr. Kaiser with a box of pralines from Belgian chocolatier Pierre Marcolini at their second meeting. Mr. Kaiser, an avowed chocoholic, returned the favor a couple of weeks later in Tulsa, giving Mr. Saverys a box of candy made by Christine Joseph, a Tulsa chocolatier who also was born in Belgium.
Convinced that Energy Bridge could work, Mr. Kaiser agreed to take over the business, closing the deal last December. El Paso paid him $75 million; in return, he assumed a $120 million obligation to Exmar. El Paso also agreed to pay to install the underwater pipeline connection that carries the gas from the ship to existing pipelines in the Gulf of Mexico.
The bulk of the $660 million Mr. Kaiser invested went to modify three specially equipped tankers and to charter them for 20 years. If Energy Bridge opens on time in January, it will be at least two and a half years ahead of any new terminals being developed by other energy companies. In addition, civic leaders in Massachusetts and Rhode Island, eager to keep LNG terminals and tankers far from the mainland, are encouraging Mr. Kaiser to build an offshore tanker-based project along the Atlantic coast of the U.S.
Mr. Kaiser, who declined requests for an interview but answered some questions by e-mail, concedes he doesn’t like "taking a risk on an undemonstrated technology." But he says that the chance to import natural gas quickly was "such an obvious and alluring business opportunity" that he felt compelled to get Energy Bridge into operation. He’s betting that new LNG-export facilities expected to come online next year in Egypt, Trinidad and Nigeria will create enough extra supply to provide him with ample LNG.
. . .
He says he acquired Energy Bridge as a challenge. "I don’t gain much pleasure from personal expenditure or recognition," he wrote in an e-mail. "And any gains I make from the enterprise will accrue to charity. But I enjoy problem solving and I want to keep my brain active to forestall (or at least diminish) atrophy."
For the full story, see:
Russell Gold. "Liquid Assets: A Billionaire Takes a Gamble To Fix Natural-Gas Shortage; Mr. Kaiser Plans to Shift Processing Onto Tankers, Avoiding Terrorism Fears; A Deal Sealed With Sweets." The Wall Street Journal (Fri., July 23, 2004): A1 & A6.
(Note: ellipses added.)


 The skin of Timothy Hall’s hands melted together in a coal mine accident in September 2005. Source of image: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
The skin of Timothy Hall’s hands melted together in a coal mine accident in September 2005. Source of image: online version of the WSJ article cited below.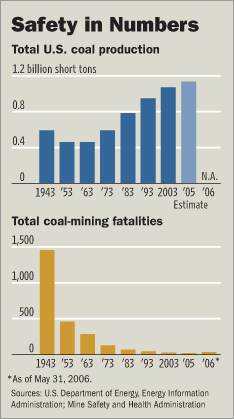 Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited above.
Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited above.




 Upper left is retired banker Leon Reinhart. Lower right is Bill Saturno, who’s archeology dig is being funded by Reinhart. Source of photos: online version of WSJ article cited below.
Upper left is retired banker Leon Reinhart. Lower right is Bill Saturno, who’s archeology dig is being funded by Reinhart. Source of photos: online version of WSJ article cited below.
 Scenes from the Georgia Aquarium. Source of photos: online version of the NYT article cited below.
Scenes from the Georgia Aquarium. Source of photos: online version of the NYT article cited below.
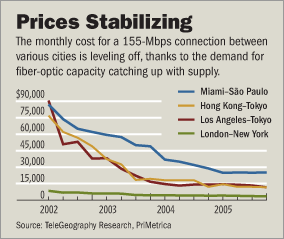 Source of graphic: online version of WSJ article cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of WSJ article cited below.