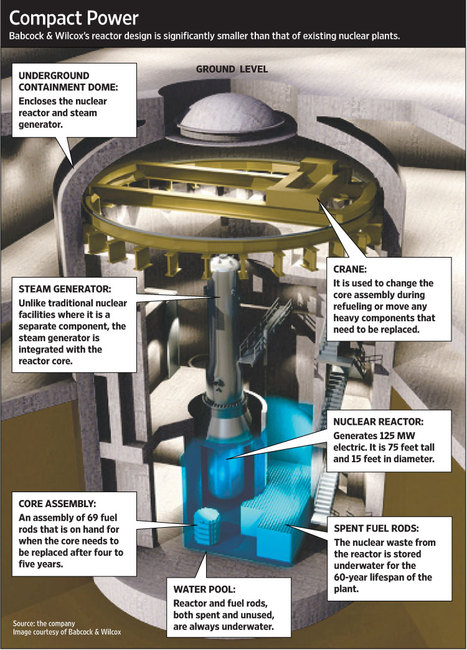
“Rising Currents: Projects for New York’s Waterfront In this MoMA show, a model by Architecture Research Office marries a wholly new landscape to Lower Manhattan’s streets.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
“Rising Currents: Projects for New York’s Waterfront In this MoMA show, a model by Architecture Research Office marries a wholly new landscape to Lower Manhattan’s streets.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
Much is in doubt about “global warming” including how much the globe will warm, and how fast, to what extent the benefits of global warming would balance the costs, and what actions (such as Nathan Myhrvold’s creative plan) might be taken to counteract global warming.
But one certainty is that if governments leave innovative entrepreneurial capitalism alone, human creativity will find ways to adapt in order to increase the benefits and reduce the costs.
Few cities have displayed as much creative destruction in architecture as New York. (One book on New York architecture was even called The Creative Destruction of Manhattan“). The article quoted below describes some visions of how New York City might adapt to an increase in sea level that might result from global warming.
(p. C21) “Rising Currents: Projects for New York’s Waterfront,” a new show at the Museum of Modern Art, reflects a level of apocalyptic thinking about this city that we haven’t seen since it was at the edge of financial collapse in the 1970s, a time when muggers roamed freely, and graffiti covered everything.
Organized by Barry Bergdoll, the Modern’s curator of architecture and design, the show is a response to the effects that rising sea levels are expected to have on New York City and parts of New Jersey over the next 70 or so years, according to government studies. The solutions it proposes are impressively imaginative, ranging from spongelike sidewalks to housing projects suspended over water to transforming the Gowanus Canal into an oyster hatchery.
. . .
(p. C23) A general interest in re-examining parts of the urban fabric that we take for granted, like streets, piers and canals — as opposed to the more familiar desire to create striking visual objects — is one of the main strengths of the exhibition. A team led by Matthew Baird Architects, for example, has focused on a huge oil refinery in Bayonne, N.J., that, if current estimates hold, will be entirely under water before our toddlers have hit retirement age. Rather than taking the predictable and bland route of transforming the industrial site into a park, the team proposes a system of piers that would support bio-fuel and recycling plants, including one that would produce the building blocks for artificial reefs out of recycled glass.
Those large, multipronged objects, which the architects call “jacks,” could be dumped off boats in strategically chosen locations, where their forms would naturally interlock to create artificial reefs once they settled at the bottom of the harbor. The jacks are magical objects, at once tough and delicate, and when you see examples of them from across the room at MoMA, their heavy legs and crushed glass surfaces make them look almost like buildings.
But here again, what’s really commendable about the design is the desire to look deeper into how systems — in this case, global systems, both natural and economic — work. According to Mr. Baird’s research, the melting of the ice cap could one day create a northern shipping passage that would make New York Harbor virtually obsolete. The manufacturing component of the design is meant as part of a broader realignment of the city’s economy that anticipates that shift.
For the full story, see:
NICOLAI OUROUSSOFF. “Architecture Review; The Future: A More Watery New York.” The New York Times (Fri., March 26, 2010): C21 & C23.
(Note: ellipsis added.)
(Note: The online version of the article is dated March 25, 2010 and has the title “Architecture Review; ‘Rising Currents: Projects for New York’s Waterfront’; Imagining a More Watery New York.”)
The book I mention in my comments is:
Page, Max. The Creative Destruction of Manhattan, 1900-1940. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2000.