Guillaume Santacruz is among many French entrepreneurs now using London as their base. He said of his native France, “The economy is not going well, and if you want to get ahead or run your own business, the environment is not good.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
Guillaume Santacruz is among many French entrepreneurs now using London as their base. He said of his native France, “The economy is not going well, and if you want to get ahead or run your own business, the environment is not good.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
(p. 1) Guillaume Santacruz, an aspiring French entrepreneur, brushed the rain from his black sweater and skinny jeans and headed down to a cavernous basement inside Campus London, a seven-story hive run by Google in the city’s East End.
. . .
A year earlier, Mr. Santacruz, who has two degrees in finance, was living in Paris near the Place de la Madeleine, working in a boutique finance firm. He had taken that job after his attempt to start a business in Marseille foundered under a pile of government regulations and a seemingly endless parade of taxes. The episode left him wary of starting any new projects in France. Yet he still hungered to be his own boss.
He decided that he would try again. Just not in his own country.
“A lot of people are like, ‘Why would you ever leave France?’ ” Mr. Santacruz said. “I’ll tell you. France has a lot of problems. There’s a feeling of gloom that seems to be growing deeper. The economy is not going well, and if you want to get ahead or run your own business, the environment is not good.”
. . .
(p. 5) “Making it” is almost never easy, but Mr. Santacruz found the French bureaucracy to be an unbridgeable moat around his ambitions. Having received his master’s in finance at the University of Nottingham in England, he returned to France to work with a friend’s father to open dental clinics in Marseille. “But the French administration turned it into a herculean effort,” he said.
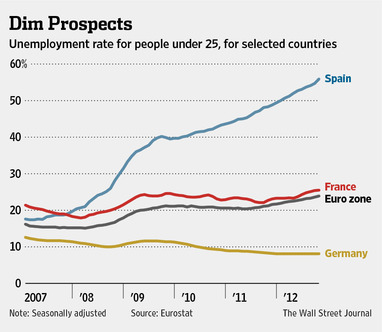
A one-month wait for a license turned into three months, then six. They tried simplifying the corporate structure but were stymied by regulatory hurdles. Hiring was delayed, partly because of social taxes that companies pay on salaries. In France, the share of nonwage costs for employers to fund unemployment benefits, education, health care and pensions is more than 33 percent. In Britain, it is around 20 percent.
“Every week, more tax letters would come,” Mr. Santacruz recalled.
. . .
Diane Segalen, an executive recruiter for many of France’s biggest companies who recently moved most of her practice, Segalen & Associés, to London from Paris, says the competitiveness gap is easy to see just by reading the newspapers. “In Britain, you read about all the deals going on here,” Ms. Segalen said. “In the French papers, you read about taxes, more taxes, economic problems and the state’s involvement in everything.”
. . .
“It is a French cultural characteristic that goes back to almost the revolution and Robespierre, where there’s a deep-rooted feeling that you don’t show that you make money,” Ms. Segalen, the recruiter, said. “There is this sense that ‘liberté, égalité, fraternité’ means that what’s yours should be mine. It’s more like, if someone has something I can’t have, I’d rather deprive this person from having it than trying to work hard to get it myself. That’s a very French state of mind. But it’s a race to the bottom.”
For the full story, see:
LIZ ALDERMAN. “Au Revoir, Entrepreneurs.” The New York Times, SundayBusiness Section (Sun., MARCH 23, 2014): 1 & 5.
(Note: ellipses added.)
(Note: the online version of the story has the date MARCH 22, 2014.)
 ‘Diane Segalen moved most of her executive recruiting practice to London from Paris. In France, she says, “there is this sense that ‘liberté, égalité, fraternité’ means that what’s yours should be mine.”” Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.
‘Diane Segalen moved most of her executive recruiting practice to London from Paris. In France, she says, “there is this sense that ‘liberté, égalité, fraternité’ means that what’s yours should be mine.”” Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.