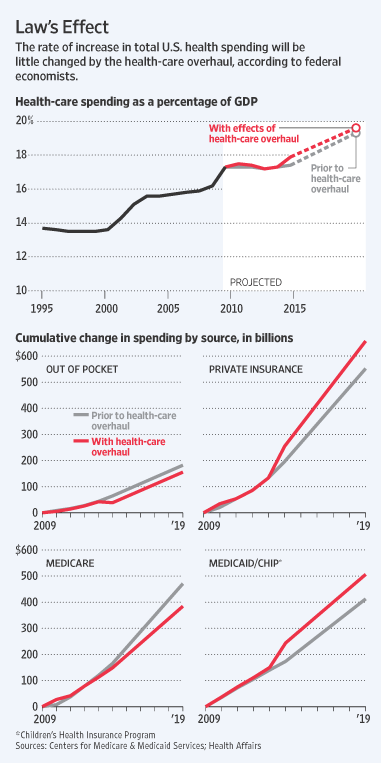
Entrepreneur Joe Ricketts. Source of photo: online version of the Omaha World-Herald article quoted and cited below.
I used to teach an Economics of Technology course in the UNO EMBA program (until a curriculum committee axed the course). As a long-shot I once invited Joe Ricketts to speak to the class. I was surprised that he accepted, and maybe also surprised that he clearly invested some time and thought in his presentation. The class was riveted not only by the story of his own entrepreneurial challenges, but also of his views of the policy issues of the day. I remember his good-natured persistence in arguing with one student who challenged him on his view of the importance of tort-reform.
From his manner, and some of the stories he told, he seemed to be the sort of entrepreneur who exemplified George Gilder’s view that great entrepreneurs have a kind of humility that leaves them open to learning, at least in key areas related to their business goals. By all accounts, Sam Walton was another example. And I heard Charles Koch speak this summer and saw him interact with some of his executives; he also gave the impression of being down-to-earth, and open to learning.
(Of course, then there’s Steve Jobs and Larry Ellison—generalizations on entrepreneurship are hard to come by!)
Ricketts and Koch also share another trait—this one too rare among successful entrepreneurs. They are both willing to invest a considerable part of their hard-earned wealth in order to preserve and protect the institutions of limited government that will make it possible for future entrepreneurs to succeed. In Ricketts’ case, for example:
(p. 7A) WASHINGTON — Joe Ricketts wants to bring down at least one Capitol Hill lawmaker who seeks earmarks so he can get the rest of Congress’ attention.
The founder and former CEO of what is now TD Ameritrade has started a new organization called Taxpayers Against Earmarks, which will seek to highlight what he describes as the evils of legislators setting aside money for pet projects back home.
. . .
Ricketts said that while some earmarks support worthy projects, he is against them all because the process is flawed. He compared those who support earmarks to addicts and criminals.
“I’m sure that all over the country there are people that like earmarks and people come to defend earmarks, and those are the people that are on the dope,” he said.
Ricketts said those who seek earmarks are asking legislators to spend other people’s money for their purposes.
“That’s theft,” he said. “As Tom Coburn says, that’s intergenerational theft. So those people that like earmarks, you can consider thieves.”
. . .
Ricketts said . . . the process encourages lawmakers to throw their support behind other spending bills to gain other lawmakers’ support for their earmarks.
“A lot of elected officials like the earmarks, but they’ve never had anybody like me or anybody else push back. … So now the scales are going to balance a little bit,” he said. “I’m going to spend as many years and as many dollars as it takes to be successful.”
For the full story, see:
Joseph Morton. “Joe Ricketts Will Put Up Big Bucks to Fight Earmarks.” Omaha World-Herald (Friday, October 1, 2010): 7A.
(Note: all ellipses added, except for the last one which was in the original.)
(Note: the online version of the article has the title “Joe Ricketts will help fight earmarks.”)