(p. D2) . . . most of the horror-movie scenarios are looking less and less plausible. Climate change will probably occur not with a bang but with a long, slow whimper, as you can see in the new report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
The report concludes that it’s ”very likely” that humans are now the main factor warming the climate. But even as the panel’s scientists are becoming surer of the problem, and warning of grim consequences this century and beyond, they’re eschewing crowd-thrilling catastrophes. Since the last I.P.C.C. report, six years ago, they haven’t raised the estimates of future temperatures and sea levels.
While Mr. Gore’s movie shows coastlines flooded by a 20-foot rise in sea level, the report’s projections for the rise this century range from 7 inches to 23 inches. The panel says Greenland’s ice sheet will shrink and might eventually disappear, but the process could take ”millennia.” The Antarctic ice sheet is projected to grow, not shrink, because of increased snowfall.
The scientists acknowledge uncertainties and worrisome new signs, like the sudden acceleration in the flow of Greenland’s glaciers several years ago. But the panel, unlike Mr. Gore, didn’t extrapolate a short-term trend into a disaster, and its caution is vindicated by a report in the current issue of Science that the flow of two of the largest glaciers abruptly decelerated last year to near the old rate.
The panel does consider it ”likely” that future typhoons and hurricanes will be stronger than today’s. But it also expects fewer of these storms (albeit with ”less confidence” in that projection).
As for the Gulf Stream, it is ”very unlikely” to undergo ”a large abrupt transition during the 21st century,” according to the new report. The current is expected to slow slightly, meaning a little less heat from the tropics would reach the North Atlantic, which could be good news for Europe and North America, since that would temper some of the impact of global warming in the north.
Whatever happens, you can stop fretting about the Gulf Stream scenario in Mr. Gore’s movie and that full-fledged Hollywood disaster film ”The Day After Tomorrow.” Mr. Gore’s companion book has a fold-out diagram of the Gulf Stream and warns that ”some scientists are now seriously worried” about it shutting down and sending Europe into an ice age, but he must have been talking to the wrong scientists.
There wouldn’t be glaciers in the English shires even if the Gulf Stream did shut down. To understand why, you need to disregard not only the horror movies but also what you learned in grade school: that the Gulf Stream is responsible for keeping London so much warmer than New York even though England is farther north than Newfoundland.
This theory, originated by a 19th-century oceanographer, is ”the earth-science equivalent of an urban legend,” in the words of Richard Seager, a climate modeler at the Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University. He and other researchers have calculated that the Gulf Stream’s influence typically raises land temperatures in the north by only five degrees Fahrenheit, hardly enough to explain England’s mild winters, much less its lack of glaciers.
Moreover, as the Gulf Stream meanders northward, it delivers just about as much heat to the eastern United States and Canada as to Europe, so it can’t account for the difference between New York and London. Dr. Seager gives the credit to the prevailing westerly winds — and the Rocky Mountains.
When these winds out of the west hit the Rockies, they’re diverted south, bringing air from the Arctic down on New York (as in last week’s cold spell). After their southern detour, the westerlies swing back north, carrying subtropical heat toward London. This Rocky Mountain detour accounts for about half the difference between New York and London weather, according to Dr. Seager.
The other half is caused by to the simple fact that London sits on the east side of an ocean — just like Seattle, which has a much milder climate than Siberia, the parallel land across the Pacific. Since ocean water doesn’t cool as quickly as land in winter, or heat up as much in summer, the westerly winds blowing over the ocean moderate the winter and summer temperatures in both Seattle and London.


 Dubai skyline. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ commentary quoted and cited below.
Dubai skyline. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ commentary quoted and cited below.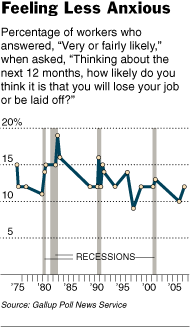 Source of graph: online version of the NYT article cited below.
Source of graph: online version of the NYT article cited below.