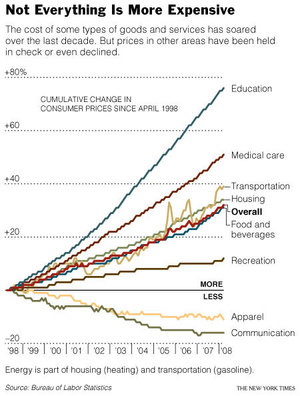
Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
(p. B1) Corning Inc. has survived for 157 years by betting big on new technologies, from ruby-colored railroad signals to fiber-optic cable to flat-panel TVs. And now the glass and ceramics manufacturer is making its biggest research bet ever.
Under pressure to find its next hit, the company has spent half a billion dollars — its biggest wager yet — that tougher regulations in the U.S., Europe and Japan will boost demand for its emissions filters for diesel cars and trucks.
. . .
An investment 25 years ago has turned Corning into the world’s largest maker of liquid-crystal-display glass used in flat-panel TVs and computers. But another wager, which made it the biggest producer of optical fiber during the 1990s, almost sank the company when the tech boom turned into a bust.
In Erwin, a few miles from the company’s headquarters in Corning, the glassmaker is spending $300 million to ex-(p. B2)pand research labs. There, some 1,700 scientists work on hundreds of speculative projects, from next-generation lasers to optical sensors that could speed the discovery of drugs.
“Culturally, they’re not afraid to invest and lose money for many years,” says UBS analyst Nikos Theodosopoulos. “That style is not American any more.”
Corning also goes against the grain in manufacturing. While it has joined the pack in moving most of its production overseas, it eschews outsourcing and continues to own and operate the 50 factories that churn out thousands of its different products.
Corning argues that retaining control of research and manufacturing is both a competitive advantage and a form of risk management. Its strategy is to keep an array of products in the pipeline and, once a market develops, to build factories to quickly produce in volumes that keep rivals from gaining traction.
For the full story, see:
SARA SILVER. “Corning’s Biggest Bet Yet? Diesel-Filter Technologies.” The Wall Street Journal (Fri., March 7, 2008): B1-B2.
(Note: ellipsis added.)

“Corning DuraTrap diesel-engine filter.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited above.