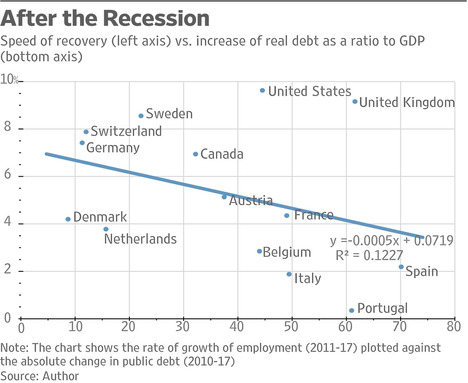
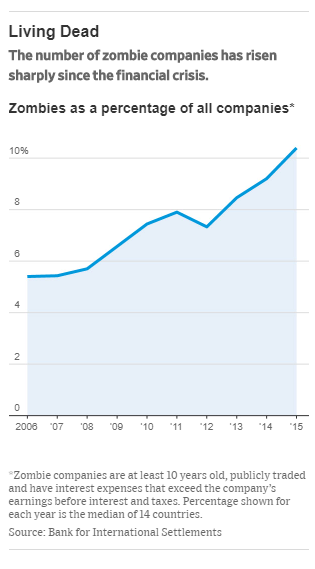
(p. A17) As the economist Joseph Schumpeter observed: “The capitalist process, not by coincidence but by virtue of its mechanism, progressively raises the standard of life of the masses.”
For Schumpeter, entrepreneurs and the companies they found are the engines of wealth creation. This is what distinguishes capitalism from all previous forms of economic society and turned Marxism on its head, the parasitic capitalist becoming the innovative and beneficent entrepreneur. Since the 2008 crash, Schumpeter’s lessons have been overshadowed by Keynesian macroeconomics, in which the entrepreneurial function is reduced to a ghostly presence. As Schumpeter commented on John Maynard Keynes’s “General Theory” (1936), change–the outstanding feature of capitalism–was, in Keynes’s analysis, “assumed away.”
Progressive, ameliorative change is what poor people in poor countries need most of all. In “The Prosperity Paradox: How Innovation Can Lift Nations Out of Poverty,” Harvard Business School’s Clayton Christensen and co-authors Efosa Ojomo and Karen Dillon return the entrepreneur and innovation to the center stage of economic development and prosperity. The authors overturn the current foreign-aid development paradigm of externally imposed, predominantly government funded capital- and institution-building programs and replace it with a model of entrepreneur-led innovation. “It may sound counterintuitive,” the authors write, but “enduring prosperity for many countries will not come from fixing poverty. It will come from investing in innovations that create new markets within these countries.” This is the paradox of the book’s title.
Continue reading “Innovative Entrepreneurs Bring Prosperity to the Poor”