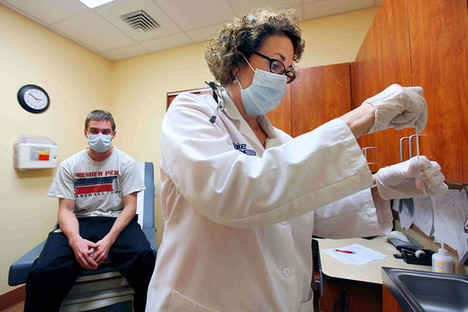
“Amir Jahan found her health insurance wouldn’t pay for all of her $200 stomach surgery; she continues to work with an untreated tumor.” Source of caption: print version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
“Amir Jahan found her health insurance wouldn’t pay for all of her $200 stomach surgery; she continues to work with an untreated tumor.” Source of caption: print version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
(p. A14) PANIPAT, India — Amir Jahan can spin thick, white thread into magnificent cloth, but the 46-year-old weaver has been unable to unravel her health plan to pay for stomach surgery.
Under a health-insurance program introduced a few years ago, the Indian government has provided health-insurance coverage for the country’s hand-loom weavers, a group of 6.5 million workers, 60% of them female, who are mostly illiterate and invariably poor. Yet holding an insurance card hasn’t helped Ms. Jahan, who says the coverage only pays for minor ailments and not for major problems, such as the removal of a stomach tumor.
“The health care is all a sham,” Ms. Jahan says angrily. “I was refused treatment on grounds of huge expense. I won’t ever go to be humiliated again.”
Ms. Jahan’s health-care issues represent the problems that come with trying to provide insurance to India’s poor. Access to quality care remains a distant dream for many in this country of 1.1 billion.
Last year, the Indian government launched the National Health Insurance Program on (sic) promised health coverage of $700 per person for families earning less than $100 a year.
Holders of health cards have to register in their home states to access benefits, thereby precluding a large population of migrant laborers. Those who can get past the complex state-identification and qualification process often can’t cope with hospital bureaucracies.
For the full story, see:
VIBHUTI AGARWAL. “Indian Weavers Shun Health Plan.” The Wall Street Journal (Sat., Sept., 2009): A14.