Cairo entrepreneur serves good food to willing customers. Source of image: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
Cairo entrepreneur serves good food to willing customers. Source of image: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
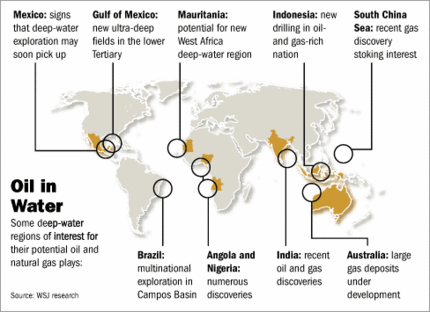
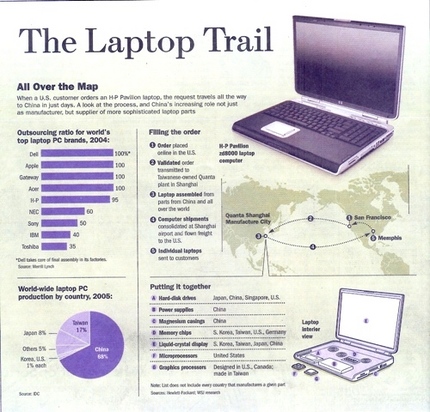
In The Other Path, Hernando de Soto wrote about how governments in much of the world make it nearly impossible for the poor to legally get a start as entrepreneurs. Here is a perfect example of de Soto’s point:
CAIRO, Oct. 2 — With his cart tucked beneath a highway overpass, just beside the railroad tracks and behind a parked taxi, Farouk Salem darted his eyes back and forth nervously as he awaited customers.
On most days, except during Ramadan, the sun has barely risen and worshipers are shuffling out of the nearby mosque after morning prayers as the first customers make their way to Mr. Salem. A few quick flicks of a ladle, the shaking of a bottle or two, and breakfast is ready.
Mr. Salem sells ful, the fava bean stew that is a staple of Egyptian cuisine, as a cheap, hearty breakfast for just 20 cents. But he is an unlicensed street vendor, one of the many hundreds of thousands of Egyptians who make their living in what economists here describe as Egypt’s informal work force: selling, delivering, cooking, cleaning, serving, ferrying, shoeshining, anything that will provide income.
Dr. Rashad Abdou, a professor of economics at Cairo University, estimated that the informal sector might account for as much as 60 percent of Egypt’s economy.
“As long as I keep a low profile, they don’t bother me,” Mr. Salem said on a recent day, as his brother worked behind the parked metal cart, dishing out bowls of ful. The police have forced him to move many times and have even confiscated his cart. But it is hard to keep a really low profile when the food is good and the prices are cheap.
As the sun began to heat up the morning air, customers showed up in a steady stream, some still in their pajamas.
“It’s good,” said Muhammad Abbadi. “It’s clean. And the most important thing is it’s cheap. We are poor. You see how poor we are in Egypt.”
. . .
“If the authorities want to chase me away, they will do it,” he says, his face tight and nervous. “If they want to put me in prison, they can. If they want to take my cart away, they can.”
He walked over to get some more bread as Muhammad kept ladling.
For the full story, see:
MICHAEL SLACKMAN. "CAIRO JOURNAL; A Hand on the Ladle, and an Eye Out for the Law." The New York Times (Tues., October 3, 2006): A4.
(Note: ellipses added.)
 Ful is a fava bean stew that is popular in Cairo. Source of image: online version of the NYT article cited above.
Ful is a fava bean stew that is popular in Cairo. Source of image: online version of the NYT article cited above.
The reference to the de Soto book is:
Soto, Hernando de. The Other Path: The Invisible Revolution in the Third World. 1st ed: HarperCollins, 1989.



 Ful is a fava bean stew that is popular in Cairo. Source of image: online version of the NYT article cited above.
Ful is a fava bean stew that is popular in Cairo. Source of image: online version of the NYT article cited above.

 Hernando de Soto and Bill Clinton at the second annual Clinton Global Initiative. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
Hernando de Soto and Bill Clinton at the second annual Clinton Global Initiative. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article cited below.

 Source of graphic: online version of the NYT article cited above.
Source of graphic: online version of the NYT article cited above.