(p. A1) JUCHITÁN, Mexico — For as long as anyone can remember, shopping for many items in this Zapotec Indian town meant lousy selection and high prices. Most families live on less than $4,000 a year. Little wonder that this provincial corner of Oaxaca, historically famous for keeping outsiders at bay, welcomed the arrival of Wal-Mart.
Back home in the U.S., Wal-Mart Stores Inc. is known not only for its relentless focus on low prices but also for its many critics, who assail it for everything from the wages it pays to its role in homogenizing American culture. But while its growth in the U.S. is slowing, Wal-Mart is striking gold south of the border, largely free from all the criticism. Like Wal-Mart fans in less affluent parts of America, most shoppers in developing countries are much more concerned about the cost of medicine and microwaves than the cultural incursions of a multinational corporation.
That fact is making Wal-Mart a dominant force in Latin America. Wal-Mart de México SAB, a publicly traded subsidiary, is not only the biggest private employer in Mexico — it’s the biggest single retailer in Latin America. Sales at Wal-Mex, as the Mexican unit is called, are forecast to rise 16% to $21 billion this year, representing a quarter of Wal-Mart’s foreign revenue. International revenue soared 30% to $77.1 billion, accounting for 22% of Wal-Mart’s sales, in the fiscal year ended Jan. 31. Wal-Mex profits are forecast to grow 20% to $1.3 billion this year.
. . .
(p. A14) In Mexico, Wal-Mart has been a counterweight to the powers that control commerce. One of the most closed economies in the world until the late 1980s, Mexico was dominated for decades by a handful of big grocers and retailers. All were members of a national retailing association called ANTAD, and cutthroat competition was taboo. At the local level, towns are still hostage to local bosses, known here as caciques, the Indian word for local strongmen who control politics and commerce.
. . .
In recent months, as rising prices for U.S. corn pushed up the price of Mexico’s corn tortilla, a staple for millions of poor, Wal-Mart could keep tortilla prices largely steady because of its long-term contracts with corn-flour suppliers. The crisis turned into free advertising for Wal-Mart, as new shoppers lined up for the cheaper tortillas.
Wal-Mart also overcame a Juchitán cacique, or local boss: Héctor Matus, a trained doctor who goes by La Garnacha, the name for a fried tortilla snack popular in town. Dr. Matus, 55, owns six pharmacies, stationery stores and general stores. He has also held an array of political posts, including Juchitán mayor and state health minister. As town mayor from 2002 to 2004, he says he blocked a national medical-testing chain from opening in town because it meant low-price competition to local businessmen doing blood work.
But Dr. Matus couldn’t persuade local and state officials to block Wal-Mart, and he is feeling the pinch. Sales are off 15% at his stores since Wal-Mart arrived, and he is now lowering prices in response. Even so, he’s still more expensive. A box of Losec stomach medicine costs 80 pesos ($7.30) at one of Dr. Matus’s stores, marked down from 86 pesos. The price at Wal-Mart is 77 pesos ($7.20).
Dr. Matus isn’t happy about the competition. "I could still kick them out of town, because I know how to mobilize people," he said, sitting in his living room surrounded by pictures of him with leading Mexican politicians dating back to the 1970s. Despite his bravado, town officials say Wal-Mart is staying. "The ones who have benefited the most [from Wal-Mart] are the poorest," says Feliciano Santiago, the deputy mayor. "I hope another one comes."
. . .
Gisela López, the 31-year-old head of billing at the Juchitán store, benefited from the retailer’s system of promoting from within. Raised by her uneducated, Zapotec-speaking grandparents, Ms. López earned a computer degree at Juchitán’s small technical college and then left for the booming northern city of Monterrey in search of opportunity.
Lacking connections, she couldn’t find the office job she dreamed about, and took a job at one of Wal-Mart’s stores. After three months, Ms. López made cashier supervisor, and later moved over to the billing department. When Wal-Mart opened a store in Juchitán, Ms. López jumped at the chance to move home — and was promoted to billing chief in the process.
"It’s a very different place to work, because you can succeed by your own effort," says Ms. López, whose $12,000-a-year salary now puts her in Mexico’s middle class.
Ms. López’s story of economic mobility is a rare one. Most of her childhood friends don’t have steady jobs, she said. The success stories are friends who inherited jobs from their parents at the state oil company’s big refinery in Salina Cruz, about an hour away.
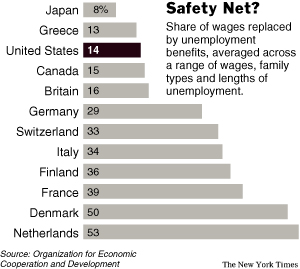 Source of graphic: online version of the NYT article cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of the NYT article cited below.



 Work and non-work at Google’s Manhattan offices. Source of photos: online version of the NYT article cited above.
Work and non-work at Google’s Manhattan offices. Source of photos: online version of the NYT article cited above.
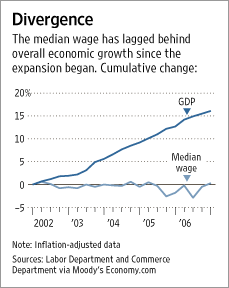 Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited above.
Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited above.
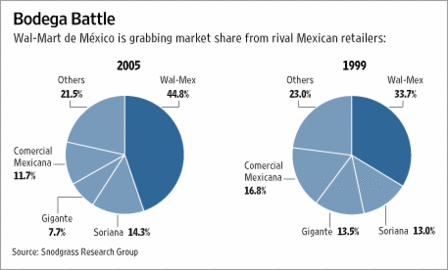

 Source of map and images: online version of the WSJ article cited above.
Source of map and images: online version of the WSJ article cited above.