From Episode #519 of The West Wing, which was written by Eli Attie, directed by Richard Schiff, and first aired on NBC on Wednesday, April 21, 2004, during the fifth season:
Josh has negotiated a trade deal. The President is enthused about the agreement and he and Leo are looking now at getting it through Congress. But when C.J. asks what he is going to say to those who say the agreement is going to export jobs, Bartlet makes a joke about economists recommending filing for unemployment. So, Josh asks,
“Sir, have you read the talking points?”
“I’m an economist. Some would say half-decent. I don’t need a primer on this.”
“Due respect,sir,” Charlie says as a lead-in to, “your answers on economics can be a bit—” When he hesitates for a fraction of a second, Bartlet offers a word.
“Polysyllabic?”
“Academic,” C.J. counters.
“I was going to go with incomprehensible,” says Leo.
“Hey listen: Any economic advancement involves what Schumpeter called ‘creative destruction’.”
“…Not a good answer,” C.J. tells him. “…’Cause that word ‘destruction will really mollify our critics….”
“Global economic forces are unstoppable just like technology itself,” Bartlet insists.
But C.J. and Josh counter that the answers to everything must be, “Free trade produces better, higher paying jobs. It’s got to be that simple.”
The source of the transcription of the above dialogue is: http://westwing.bewarne.com/fifth/519points.html
(I appreciate Matt Hunter alerting me to this mention of Schumpeter, and providing me with the above link.)





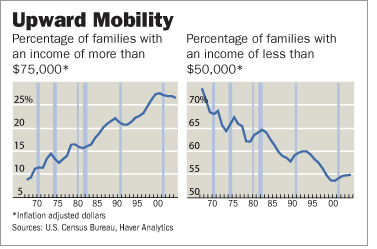 Graph source: online version of WSJ article cited below.
Graph source: online version of WSJ article cited below. 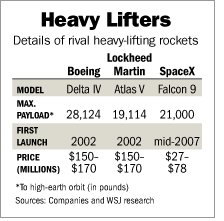 Source of table: online version of WSJ article cited below.
Source of table: online version of WSJ article cited below.