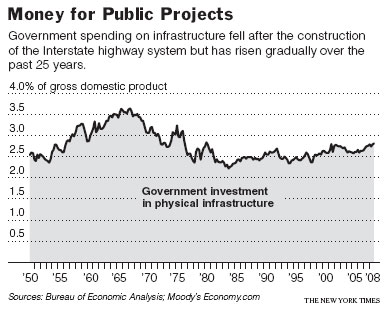
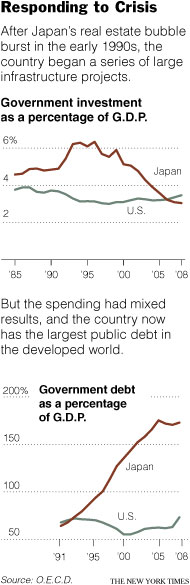
At a “Workshop on Creative Ideas to Teach Principles,” organized by Jim Gwartney at the Stavros Center in Tampa, I presented some brief video clips that I use to make various points in my principles classes. The first was Hugh Laurie’s Protest Song.
After playing the song, I tell my students that to make the world better, you need more than a guitar and good intentions—you also need to know something about how the world works (in particular, you need to know some economics).
After my presentation, one of the participants asked if I knew where he could find the lyrics. In response, I found the lyrics posted online, and re-post them here in case they may be of use to other economic educators.
Hugh Laurie’s Saturday Night Live Protest Song
[ open on Hugh Laurie standing at Home Base strumming a guitar ]
Hugh Laurie: This is a protest song. [ blows on a harmonica attached to his neck ]
[ singing ]
“Well, the poor keep getting hungry, and the rich keep getting fat
Politicians change, but they’re never gonna change that.
Girl, we got the answer, it’s so easy you won’t believe
All we gotta do is.. [ mumbles incoherently ]
Well, the winds of war are blowin’, and the tide is comin’ in
Don’t you be hopin’ for the good times, because the good times have already been.
But, girl, we got the answer, it’s so easy you won’t believe
All we gotta do is.. [ mumbles incoherently ]
It’s so easy, to see
If only they’d listen, to you and me.
We got to.. [ mumbles incoherently ] as fast as we can
We got to.. [ mumbles incoherently ] every woman, every man
We got to.. [ mumbles incoherently ] time after time
We got to.. [ mumbles incoherently ] vodka and lime.
Well, the world is gettin’ weary, and it wants to go to bed
Everybody’s dyin’, except the ones who are already dead.
Girl, we got the answer, starin’ us right in the face
All we gotta do is
All we gotta do is
All we gotta do is.”
[ pauses, then blows on the harmonica and finishes ]
[ the audience cheers wildly ]
Hugh Laurie: Thank you.
Source of lyrics:
http://snltranscripts.jt.org/06/06dprotest.phtml