My only major disagreement with the commentary below, is that I have much more confidence that, given free market institutions, our descendants will have the incentives, energy, and ingenuity, to solve the problems that they will face.
The Stern Review’s most influential critic has probably been William Nordhaus, a 65-year-old Yale professor who is as mainstream as economists come. Jeffrey D. Sachs, the anti-poverty advocate, calls Mr. Nordhaus “about the most reasonable man I know.”
He was the first speaker after lunch, and, of course, he had some very nice things to say about Sir Nicholas. The report “was presented here very eloquently by a distinguished scholar,” Mr. Nordhaus said. But then came the juicy stuff: the Stern Review “commits cruel and unusual punishment on the English language,” Mr. Nordhaus said, and the British government’s opinion on climate change is no more infallible than was its prewar view about weapons of mass destruction in Iraq.
This was fairly tame compared with the comments of another Yale economist, Robert O. Mendelsohn. “I was awestruck,” he said, comparing Sir Nicholas to “The Wizard of Oz.” But “my job is to be Toto,” he added, in the same good-humored tone Mr. Nordhaus used. “Is it in fact The Wizard of Oz, or is it nothing at all?”
The two professors raised some questions about the science in the Stern Review. Mr. Nordhaus wondered if carbon emissions and temperatures would rise as quickly as the report suggests, and Mr. Mendelsohn predicted that people would learn to adapt to climate change, reducing its ultimate cost.
But their main objection revolved around something called the discount rate. The Stern Review assumed that a dollar of economic damage prevented a century from now (adjusted for inflation) is roughly as valuable as a dollar spent reducing emissions today. In effect, the report argues for spending the money to cut emissions because future generations have as much claim on resources as current generations. “I’ve still not heard a decent ethical argument” for believing otherwise, Sir Nicholas said at the debate.
I’m guessing that your instinct is to agree with him. Mine certainly was. The problem is that none of us actually behave this way. If we really thought that our great-grandchild deserved our money as much as we do, we would never go out to dinner again. Instead, we would invest the $50 we would have spent on dinner, confident that it would grow over time and become perhaps $1,000 for our great-grandchild to put toward health care, education or a supercomputer. Any of that is preferable to our measly dinner.
But a dollar today truly is more valuable than a dollar a century from now. For one thing, your great-grandchild will almost certainly be richer than you are and won’t need your money as much as you do. So spending a dollar on carbon reduction today to avoid a dollar’s worth of economic damage in 2107 doesn’t make sense. We would be better off putting the money toward something likely to have a higher return than alternative energy, like education.
Technically, then, Sir Nicholas’s opponents win the debate. But in practical terms, their argument has a weak link. They are assuming that the economic gains from, say, education will make future generations rich enough to make up for any damage caused by climate change. Sea walls will be able to protect cities; technology can allow crops to grow in new ways; better medicines can stop the spread of disease.
For the full commentary, see:


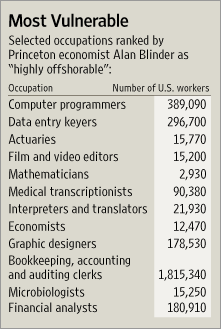 Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited below. Alan S. Blinder. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article cited above.
Alan S. Blinder. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article cited above.


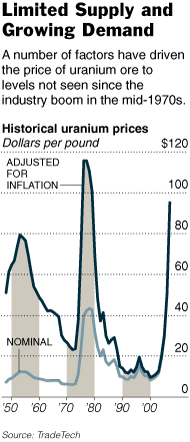 Yellowcake, which is processed uranium, is in the third jar from the left of the top photo. The photo below it is of old equipment at a dormant uranium mine. Source of the photos and the graphic: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.
Yellowcake, which is processed uranium, is in the third jar from the left of the top photo. The photo below it is of old equipment at a dormant uranium mine. Source of the photos and the graphic: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above. 

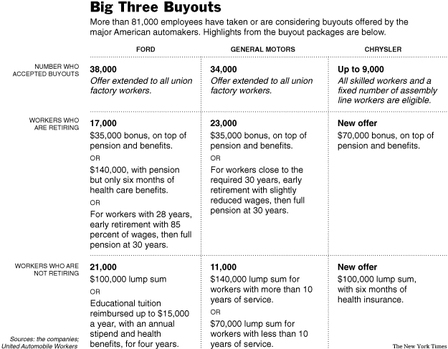

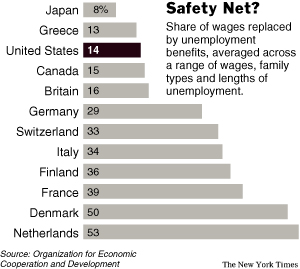 Source of graphic: online version of the NYT article cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of the NYT article cited below.
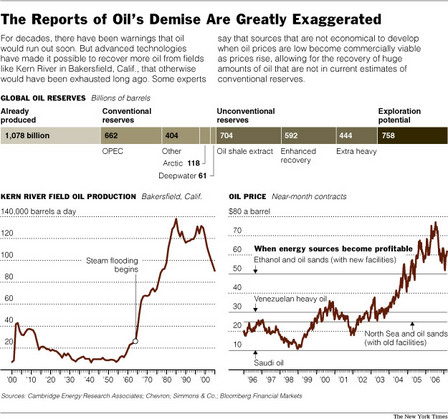
 Kern River pipelines in front, and pump in back. Source of graphic and photo: online version of the NYT article cited above.
Kern River pipelines in front, and pump in back. Source of graphic and photo: online version of the NYT article cited above.

 Work and non-work at Google’s Manhattan offices. Source of photos: online version of the NYT article cited above.
Work and non-work at Google’s Manhattan offices. Source of photos: online version of the NYT article cited above.
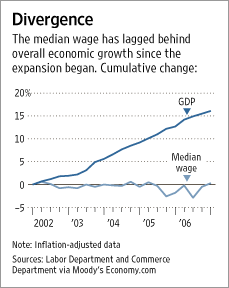 Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited above.
Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited above.