 Tall grass grows where Qingtu Lake used to be; and the desert encroaches on the grass. Source of image: online version of the NYT article cited below.
Tall grass grows where Qingtu Lake used to be; and the desert encroaches on the grass. Source of image: online version of the NYT article cited below.
(p. A1) An ever-rising tide of sand has claimed grasslands, ponds, lakes and forests, swallowed whole villages and forced tens of thousands of people to flee as it surges south and threatens to leave this ancient Silk Road greenbelt uninhabitable.
Han Chinese women here cover their heads and faces like Muslims to protect against violent sandstorms. Farmers dig wells down hundreds of feet. If they find water, it is often brackish, even poisonous.
Chinese leaders have vowed to protect Minqin and surrounding towns in Gansu Province. The area divides two deserts, the Badain Jaran and the Tengger, and its precarious state threatens to accelerate the spread of barren wasteland to the heart of China.
The national 937 Project, set up to fight the encroaching desert, estimated in April that 1,500 square miles of land, roughly the size of (p. A14) Rhode Island, is buried each year. Nearly all of north central China, including Beijing, is at risk.
Expanding deserts and a severe drought are also making this a near-record year for dust storms carried east in the jet stream. Sand squalls have blanketed Beijing and other northern cities, leaving a stubborn yellow haze in the air and coating roads, buildings, cars and lungs.
. . .
Government-led cultivation, deforestation, irrigation and reclamation almost certainly contributed to the desert’s advance, which began in the 1950’s and the 1960’s, and has accelerated. Critics warn that some lessons of past engineering fiascoes remained unlearned.
During the ill-fated Great Leap Forward in the late 1950’s, Mao ordered construction of the giant Hongyashan reservoir near Minqin, which diverted the flow of the Shiyang River and runoff from the Qilian Mountains into an irrigation system. It briefly made Minqin’s farmland fertile enough to grow grain.
But Minqin is a desert oasis that gets almost no rainfall. The Shiyang and its offshoots had been its ecological lifeline. With the available water resources monopolized for farming, nearly all other land became a target for the desert.
Today, patches of farmland that cling to irrigation channels are emerald islands in a sea of beige, an agricultural Palm Springs.
Even the irrigated plots risk extinction. Competing reservoirs on upper reaches of the Shiyang reduced its flow so severely by 2004 that the Hongyashan went dry for the first time since its construction in 1959. It was refilled after Beijing ordered an emergency diversion of water from the Yellow River, which now runs dry through much of the year here in its northern reaches.
Local officials, whose promotions in the government and Communist Party hierarchy depend more on increasing economic output than on improving the environment, have tried desperately to preserve Minqin’s farming.
. . .
"This is not a natural disaster — it is man-made," Mr. Chai said. "And unless people study the lesson of Minqin, it will repeat itself clear across China."
For the full story, see:
JOSEPH KAHN. "A Sea of Sand Is Threatening China’s Heart." The New York Times (Thurs., June 8, 2006): A1 & A14.
 Women wear headresses and face masks, not out of modesty, but to protect against the sand. Source of photo: online versio of the NYT article cited above.
Women wear headresses and face masks, not out of modesty, but to protect against the sand. Source of photo: online versio of the NYT article cited above.
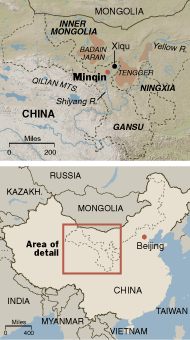 Close, and distant, maps of the areas effected. Source of maps: online version of the NYT article cited above.
Close, and distant, maps of the areas effected. Source of maps: online version of the NYT article cited above.
 One of the Viking landers on Mars. Source of photo: http://www.msss.com/mars/pictures/viking_lander/viking_lander.html
One of the Viking landers on Mars. Source of photo: http://www.msss.com/mars/pictures/viking_lander/viking_lander.html

 Bjorn Lomborg. Source of image:
Bjorn Lomborg. Source of image: 
 Source of book image: online version of WSJ article cited below.
Source of book image: online version of WSJ article cited below.

 Close, and distant, maps of the areas effected. Source of maps: online version of the NYT article cited above.
Close, and distant, maps of the areas effected. Source of maps: online version of the NYT article cited above.

 A vacuum tube used in guitar amplifiers, that was produced in the factory that Mike Matthews owned. Source of photo:
A vacuum tube used in guitar amplifiers, that was produced in the factory that Mike Matthews owned. Source of photo:  George B. Kaiser. Source of photo:
George B. Kaiser. Source of photo:  The skin of Timothy Hall’s hands melted together in a coal mine accident in September 2005. Source of image: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
The skin of Timothy Hall’s hands melted together in a coal mine accident in September 2005. Source of image: online version of the WSJ article cited below.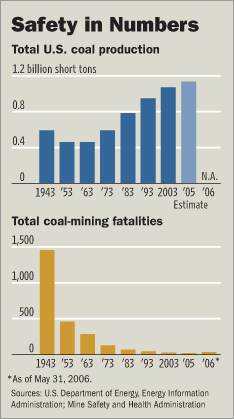 Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited above.
Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited above.