 Source of graph: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
Source of graph: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
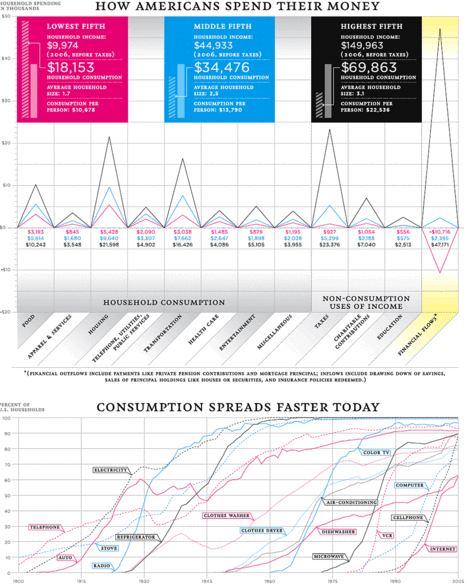
(p. 14) To understand why consumption is a better guideline of economic prosperity than income, it helps to consider how our lives have changed. Nearly all American families now have refrigerators, stoves, color TVs, telephones and radios. Air-conditioners, cars, VCRs or DVD players, microwave ovens, washing machines, clothes dryers and cellphones have reached more than 80 percent of households.
As the second chart, on the spread of consumption, shows, this wasn’t always so. The conveniences we take for granted today usually began as niche products only a few wealthy families could afford. In time, ownership spread through the levels of income distribution as rising wages and falling prices made them affordable in the currency that matters most — the amount of time one had to put in at work to gain the necessary purchasing power.
At the average wage, a VCR fell from 365 hours in 1972 to a mere two hours today. A cellphone dropped from 456 hours in 1984 to four hours. A personal computer, jazzed up with thousands of times the computing power of the 1984 I.B.M., declined from 435 hours to 25 hours. Even cars are taking a smaller toll on our bank accounts: in the past decade, the work-time price of a mid-size Ford sedan declined by 6 percent.
For the full commentary, see:
W. MICHAEL COX and RICHARD ALM. “You Are What You Spend.” The New York Times Company, Week in Review section (Sun., February 10, 2008): 14.



 "A device that U.P.S. installed in the cockpit of one of its cargo planes to display traffic information." Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.
"A device that U.P.S. installed in the cockpit of one of its cargo planes to display traffic information." Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.
 "The Independent Order of Odd Fellows, dedicated to caring for the widowed, the orphaned and the needy, is in a “state of crisis.”" Source of the photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.
"The Independent Order of Odd Fellows, dedicated to caring for the widowed, the orphaned and the needy, is in a “state of crisis.”" Source of the photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.
 "Fred Mitschele with his high-tech meter." Source of photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
"Fred Mitschele with his high-tech meter." Source of photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.



