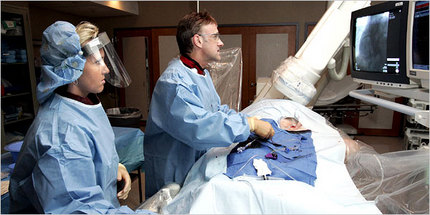
Medicare patients in Elyria receive angioplasties at a rate nearly four times the national average . . .
. . .
. . . some outside experts say they are concerned that Elyria is an example, albeit an extreme one, of how medical decisions in this country can be influenced by financial incentives and professional training more than by solid evidence of what works best for a particular patient.
“People are rewarded for erring on the side of an aggressive, highly expensive intervention,” said Dr. Elliott S. Fisher, a researcher at Dartmouth Medical School, which analyzed Medicare data and found Elyria to be an outlier.
Medicare pays Elyria’s community hospital, EMH Regional Medical Center, about $11,000 for an angioplasty involving use of a drug-coated stent.
The cardiologist might be paid an additional $800 for the work. That is well above the fees for seeing patients in the office. And with the North Ohio doctors performing thousands of angioplasties a year — about 3,400 in 2004, for example — the dollars can quickly add up.
Some medical experts say Elyria’s high rate of angioplasties — three times the rate of Cleveland, just 30 miles away — raises the question of whether some patients may be getting procedures they do not need or whether some could have been treated just as effectively and at lower cost and less risk through heart drugs that may cost only several hundred dollars a year.
. . .
Experts know that changing the financial incentives can change the way medicine is practiced.
For example, Kaiser Permanente, the big health system that employs its own doctors, says its patients in Ohio, including some in Elyria, are slightly less likely than the national average to undergo the type of cardiac procedures the North Ohio Heart Center doctors perform so prolifically.
Kaiser’s cardiologists, who work on salary instead of being paid by the procedure, typically treat patients in that region at the Cleveland Clinic, where they have hospital privileges. And they follow established protocols about when a patient should undergo an angioplasty, when drugs might suffice and when bypass surgery might be the best resort.
“It’s not just individual doctors making up their minds,” explained Dr. Ronald L. Copeland, the executive medical director for Kaiser’s medical group in Ohio. With no financial reason to perform expensive procedures, the Kaiser doctors frequently choose to manage the patients’ heart disease with drugs only. “Our doctors have no disincentive to do that,” Dr. Copeland said.
. . .
For many cardiologists, the natural tendency when they see a patient with heart disease is to perform a procedure to try to clear arterial blockages. And patients, cardiologists say, tend to rely on their doctors’ judgment.
“It’s sort of like, you go to a barber and ask if you need a haircut,” said Dr. David D. Waters, chief of cardiology at San Francisco General Hospital, who is currently studying the effectiveness of different kinds of treatment for heart disease. “He’s likely to say you do.”
. . .
Experts say it can be difficult to detect cases in which doctors cross a medical line and are clearly performing unnecessary treatments.
“A lot of decisions are discretionary,” said Dr. Harlan M. Krumholz, a cardiologist and professor at Yale.
“It’s about where the thermostat is set,” he said, arguing that doctors in a particular geographic area tend to be unaware if the way they are treating their patients is markedly different from the practices of their peers in other areas.
Traditional measures of medical quality are not set up to detect whether patients are being treated too much, he said, unlike the kinds of safeguards that prompt credit card companies to call their customers to discuss unusual spending activity. “Right now there are no ‘smart’ systems in place,” Dr. Krumholz said.
In the absence of any real monitoring or oversight, doctors in most places, including Elyria, have few incentives not to favor the treatments that provide them the most reimbursement. Dr. Waters, the San Francisco cardiologist, said that the way physicians are typically paid — more money for more procedures — results in too many decisions to give a patient a stent.
“You can’t be paying people large sums of money to do things without checks and balances,” he said.
 Salt Lake City Mayor Rocky Anderson, whose "xeriscape" yard violates a Salt Lake City zoning ordinance. Source of photo: scan from a paper copy of the NYT article cited below.
Salt Lake City Mayor Rocky Anderson, whose "xeriscape" yard violates a Salt Lake City zoning ordinance. Source of photo: scan from a paper copy of the NYT article cited below.

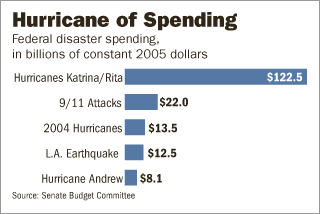 Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ editorial cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ editorial cited below.
 Source of map: online version of the NYT article cited above.
Source of map: online version of the NYT article cited above.
 Source of graphic: online version of the NYT article cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of the NYT article cited below. Canon’s new HV10 high definition camcorder. Source of image: the NYT article cited below.
Canon’s new HV10 high definition camcorder. Source of image: the NYT article cited below.