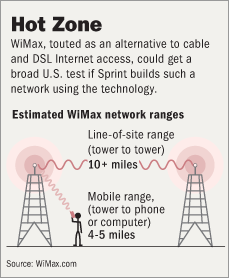
 Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
If Sprint bets on WiFi, they’re betting with their money; if the government bets on WiFi, they’re betting with your money. If Sprint succeeds, thereby benefiting the consumer, at no risk to the consumer, the consumer should not object to their earning huge profits.
Note also, that this is a plausble candidate for a firm trying to follow Clayton Christensen’s advice to try to disrupt itself. (And see the comment at the end, for someone who hasn’t read Christensen, or doesn’t believe what he has read.)
Analysts say building a nationwide WiMax network could cost Sprint between $1 billion and $4 billion, a hefty sum for a company that is already struggling to meet Wall Street’s expectations. Sprint said it expects to invest $1 billion on the project in 2007 and between $1.5 billion and $2 billion in 2008.
Sprint’s decision carries considerable risks: Investors have hammered telecom companies that have made large capital investments in new technologies, banking on future markets to emerge. For example, among other things, Verizon Communications Inc.’s stock has been under fire as the company is rolling out a costly new fiber optic network that it says will position the company to deliver a bundled TV, Internet, and phone service. Also, WiMax technology is still untested on a large scale.
Sprint is making a huge bet that consumer demand for wireless Internet access and services such as cellphone downloads of music and video will continue to grow in the coming years. Consumers already can get access to wireless Internet service at Wi-Fi "hotspots" in airports and coffee shops, and some cities, like Anaheim, Calif., are blanketing their terrain with Wi-Fi connections.
. . .
. . . , some analysts and industry experts question why the company is gearing up for such a major capital investment when it is already even or ahead the other top U.S. carriers, Verizon and Cingular Wireless, when it comes to data services. "Why compete against yourself? It doesn’t make a lot of sense at this point," said Mike Thelander, principal analyst at Signals Research Group who predicted several weeks ago that Sprint would choose WiMax.
For the full story, see:
(Note: the above passages are from the online version, which was later, and less tentative about Sprint’s intentions, than the print version.)
(Note: ellipses added.)


 Artistic vision of germ-laden hand. (This is not the photographic image mentioned below, and used as a hospital screen-saver.) Source of image: online version of the NYT article cited below.
Artistic vision of germ-laden hand. (This is not the photographic image mentioned below, and used as a hospital screen-saver.) Source of image: online version of the NYT article cited below.

 Source of book image:
Source of book image:  Source of graphic: online version of the NYT article cited above.
Source of graphic: online version of the NYT article cited above.