 The skin of Timothy Hall’s hands melted together in a coal mine accident in September 2005. Source of image: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
The skin of Timothy Hall’s hands melted together in a coal mine accident in September 2005. Source of image: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
I am not against coal. But I am puzzled why public sentiment and government policy discourage new nuclear reactors. Per unit of energy produced, isn’t nuclear safer than coal?
(p. A1) MCDOWELL, Ky. — Last September, Timothy D. Hall was drilling holes in the deepest part of a low-roofed coal mine when an explosion thrust him from his drill machine and set him on fire.
He crawled 45 feet to a mudhole inside the mine to douse the flames. The fireball melted the bill of his hard hat, charred his oxygen canister and burned his jacket, according to government investigators. After he was carried outside, but before any pain set in, he was shocked to see the flesh of his fingers had melted together.
For the full story, see:
KRIS MAHER. "Deep Trouble As Demand for Coal Rises, Risky Mines Play Bigger Role Small Operations Overall Have Higher Fatality Rates; The Dangers of ‘Dogholes’ Long-Term, a Safer Industry." The Wall Street Journal (Thurs., June 1, 2006): A1 & A10.
In the graphic below, note that the long-term trend has been a decline in fatalities in coal production. But the fatalities remain higher, per unit of energy produced, than the fatalities for nuclear energy production.
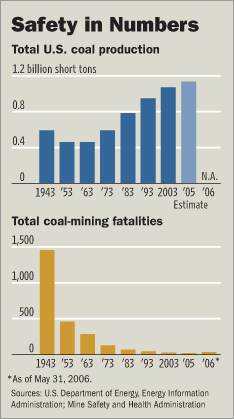 Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited above.
Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited above.



 Scenes from the Georgia Aquarium. Source of photos: online version of the NYT article cited below.
Scenes from the Georgia Aquarium. Source of photos: online version of the NYT article cited below.




 Bolivian soldiers after seizing natural gas facilities. Source of image:
Bolivian soldiers after seizing natural gas facilities. Source of image: 