 Source of graphic: scanned from p. B1 of NYT article cited below.
Source of graphic: scanned from p. B1 of NYT article cited below.
Leonard Read in his classic "I, Pencil" told the story of how the various compenents of a mere pencil came from different suppliers the world over. People who did not know each other, and might not like each other if they met, but who were brought together in productive co-operation through the power of the market. Milton Friedman frequently presented his own verison of this story. The cover of my 1980 edition of Free to Choose has a picture of Friedman holding a pencil as if in the middle of this story. And there is a short video-clip of Friedman telling the story.
A similar story could be told with many other products, and several sources have presented the raw materials in print to tell the story for laptop computers. (By "raw materials" I mean that they list the diversity of sources of the inputs; but usually without drawing all the lessons that Reed and Friedman drew.) One source is a chapter in Thomas Friedman’s The World is Flat.
Two other sources are articles that appeared within a few days of each other in The New York Times and The Wall Street Journal.
The reference to The New York Times article is:
DAVID BARBOZA. "An Unknown Giant Flexes Its Muscles; Amid Talk of Deal With I.B.M., Lenovo of China Sheds Some Obscurity." The New York Times (Sat., December 4, 2004): B1 & B3.
The reference to The Wall Street Journal article is:
Jason Dean and Pui-Wing Tam. "The Laptop Trail; The Modern PC Is a Model Of Hyperefficient Production And Geopolitical Sensitivities." The Wall Street Journal (Thurs., June 9, 2005): B1 & B8.
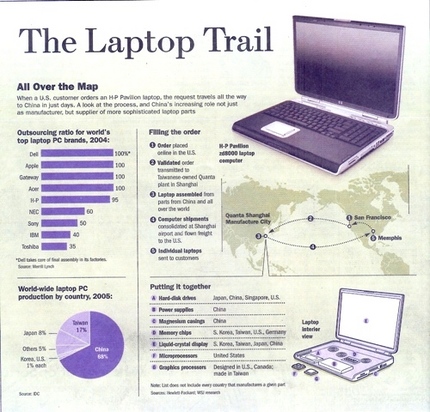 Source of graphic: scanned from p. B1 of WSJ article cited above.
Source of graphic: scanned from p. B1 of WSJ article cited above.





 Source of graphic: online version of WSJ article cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of WSJ article cited below. Hernando de Soto and Bill Clinton at the second annual Clinton Global Initiative. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
Hernando de Soto and Bill Clinton at the second annual Clinton Global Initiative. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article cited below.

 Steve Jobs at left, and Steve Wozniak at right, in San Francisco in 1977. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article cited above.
Steve Jobs at left, and Steve Wozniak at right, in San Francisco in 1977. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article cited above.