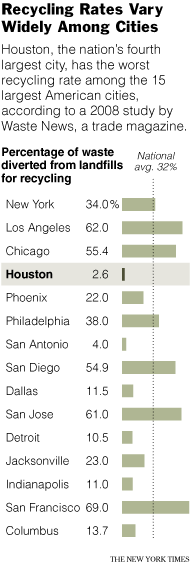
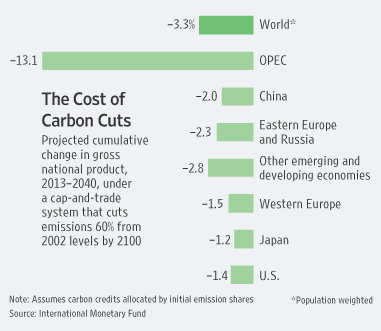
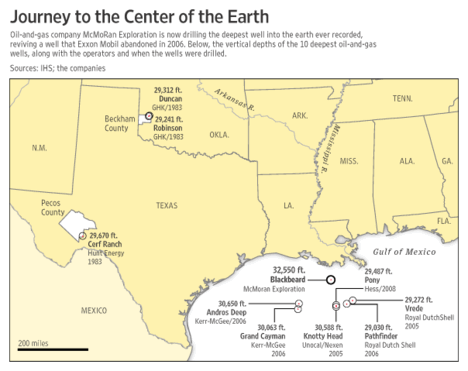
In honor of “Earth Day,” some thoughtful comments by a co-founder of Greenpeace:
(p. A23) In 1971 an environmental and antiwar ethic was taking root in Canada, and I chose to participate. As I completed a Ph.D. in ecology, I combined my science background with the strong media skills of my colleagues. In keeping with our pacifist views, we started Greenpeace.
But I later learned that the environmental movement is not always guided by science. As we celebrate Earth Day today, this is a good lesson to keep in mind.
At first, many of the causes we championed, such as opposition to nuclear testing and protection of whales, stemmed from our scientific knowledge of nuclear physics and marine biology. But after six years as one of five directors of Greenpeace International, I observed that none of my fellow directors had any formal science education. They were either political activists or environmental entrepreneurs. Ultimately, a trend toward abandoning scientific objectivity in favor of political agendas forced me to leave Greenpeace in 1986.
The breaking point was a Greenpeace decision to support a world-wide ban on chlorine. Science shows that adding chlorine to drinking water was the biggest advance in the history of public health, virtually eradicating water-borne diseases such as cholera. And the majority of our pharmaceuticals are based on chlorine chemistry. Simply put, chlorine is essential for our health.
My former colleagues ignored science and supported the ban, forcing my departure. Despite science concluding no known health risks – and ample benefits – from chlorine in drinking water, Greenpeace and other environmental groups have opposed its use for more than 20 years.
For the full commentary, see:
PATRICK MOORE. “Why I Left Greenpeace.” The Wall Street Journal (Tues., April 22, 2008): A23.