(p. A15) The Founders might have used quill pens, but they would roll their eyes at how, in this supposedly technology-minded era, we’re undermining their intention to encourage innovation. The U.S. is stumbling in the transition from their Industrial Age to our Information Age, despite the charge in the Constitution that Congress “promote the Progress of Science and useful Arts, by securing for limited Times to Authors and Inventors the exclusive Right to their respective Writings and Discoveries.”
. . .Both sides may be right. New empirical research by Boston University law professors James Bessen and Michael Meurer, reported in their book, “Patent Failure,” found that the value of pharmaceutical patents outweighed the costs of pharmaceutical-patent litigation. But for all other industries combined, they estimate that since the mid-1990s, the cost of U.S. patent litigation to alleged infringers ($12 billion in legal and business costs in 1999) is greater than the global profits that companies earn from patents (less than $4 billion in 1999). Since the 1980s, patent litigation has tripled and the probability that a particular patent is litigated within four years has more than doubled. Small inventors feel the brunt of the uncertainty costs, since bigger companies only pay for rights they think the system will protect.
These are shocking findings, but they point to the solution. New drugs require great specificity to earn a patent, whereas patents are often granted to broad, thus vague, innovations in software, communications and other technologies. Ironically, the aggregate value of these technology patents is then wiped out through litigation costs.
Our patent system for most innovations has become patently absurd. It’s a disincentive at a time when we expect software and other technology companies to be the growth engine of the economy. Imagine how much more productive our information-driven economy would be if the patent system lived up to the intention of the Founders, by encouraging progress instead of suppressing it.
For the full commentary, see:
L. GORDON CROVITZ. “OPINION: INFORMATION AGE; Patent Gridlock Suppresses Innovation.” Wall Street Journal (Mon., JULY 14, 2008): A15.
(Note: ellipsis added.)


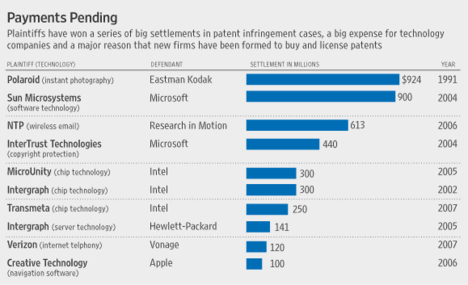


 Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited below.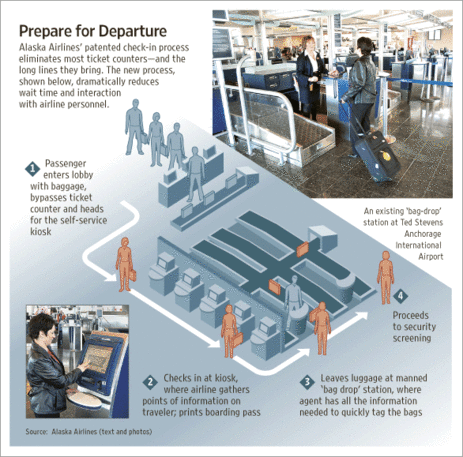



 In the photo immediately above, Don and Andrea Steirle work in their lab. The map to the left shows the location of the Berkeley Pit. Source of the photo and map: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.
In the photo immediately above, Don and Andrea Steirle work in their lab. The map to the left shows the location of the Berkeley Pit. Source of the photo and map: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above. Genentech CEO Dr. Arthur D. Levinson. Source of image: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
Genentech CEO Dr. Arthur D. Levinson. Source of image: online version of the WSJ article cited below.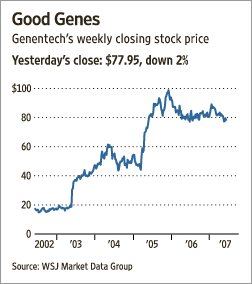 Source of graph: online version of the WSJ article cited above.
Source of graph: online version of the WSJ article cited above.