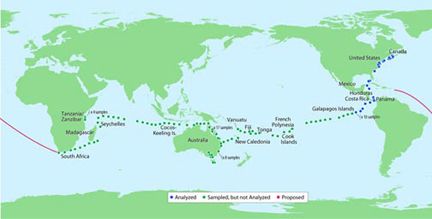
 The projected path of Venter’s Sorcerer II ship in collecting sea organisms. Source of map: http://scrippsnews.ucsd.edu/Releases/?releaseID=706
The projected path of Venter’s Sorcerer II ship in collecting sea organisms. Source of map: http://scrippsnews.ucsd.edu/Releases/?releaseID=706
Craig Venter’s private gene-sequencing effort beat the government’s effort. His new research is being funded by a $24.5 million private grant from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation. (For more information beyond the WSJ article excerpted below, see the Scripps Institution of Oceanography press release.)
(p. B1) Marine microbes are among the most abundant life form on the planet and among the most mysterious. Now, results from the first phase of a global expedition are expected to provide a glimpse into this long-hidden world while potentially leading to new drugs and even fighting climate change.
Craig Venter, the brash biologist who helped crack the human genome seven years ago, says he and other scientists have used DNA-analysis techniques to discover millions of new genes and thousands of new proteins in ocean microbes. These microscopic life forms are mainly bacteria and organisms known as archaea.
"Everything we’ve seen is a surprise," Mr. Venter said in a phone interview from his marine research vessel, Sorcerer II, in the Sea of Cortez. The unexpected variety of microbial DNA he’s found overturns earlier notions that the oceans are a homogenous soup of bacteria and other microscopic life. The details are being published today in the Public Library of Science Biology, an Internet-based scientific journal.
A diverse supply of microbial DNA from the oceans could be a rich lode for scientists. Drug companies are hunting for new compounds in sea creatures, especially to attack cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. The new data will also allow researchers to compare the DNA of oceanic bacteria to the genetic code of microorganisms that cause human disease.
"This is the largest DNA sequence ever obtained, and the magnitude of what’s being done is entirely unparalleled," said Douglas Bartlett, professor of marine microbiology at the University of California, San Diego, who isn’t involved in Dr. Venter’s project. Marine microbes "have all kind of metabolic activity. It is expected that [Dr. Venter’s team] will discover new pathways for making drugs and treating infectious disease."
For the full story, see:

 Photo on left shows Venter (on left) on his Socerer II research ship. Photo on right shows a slide of sea bacteria collected by Venter. Source of photos: http://scrippsnews.ucsd.edu/Releases/?releaseID=706
Photo on left shows Venter (on left) on his Socerer II research ship. Photo on right shows a slide of sea bacteria collected by Venter. Source of photos: http://scrippsnews.ucsd.edu/Releases/?releaseID=706



 Geologist Don Easterbrook. Source of photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.
Geologist Don Easterbrook. Source of photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above. Randall Moorehead’s Phillips Electronics wants the government to force us to switch from the incandescent bulb on the left, to bulbs like the Phillips bulb on the right. Source of photo: online version of the NYT article cited below.
Randall Moorehead’s Phillips Electronics wants the government to force us to switch from the incandescent bulb on the left, to bulbs like the Phillips bulb on the right. Source of photo: online version of the NYT article cited below. Al Gore. Source of the image: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
Al Gore. Source of the image: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below. 

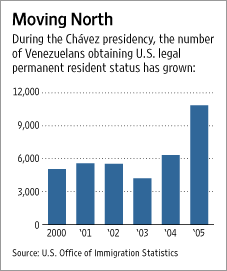 Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
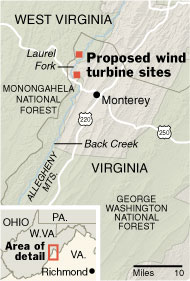 Source of map: online version of the NYT article cited above.
Source of map: online version of the NYT article cited above.
