 A poster that is displayed in some Wall Street Journal offices in solidarity with a Bancroft family member who has openly expressed doubts about Rupert Murdoch’s proposed purchase of the Journal. Source of the image: online version of the NYT article cited below.
A poster that is displayed in some Wall Street Journal offices in solidarity with a Bancroft family member who has openly expressed doubts about Rupert Murdoch’s proposed purchase of the Journal. Source of the image: online version of the NYT article cited below.
A lot of the news media imitate each other in viewpoint and content. The Wall Street Journal is fresh and innovative, and frequently gives us important news that is new.
And there have been times throughout recent decades when the editorial page of the Journal was one of the few voices for truth, justice and freedom. It would be a great loss for that voice to be silenced.
On the other hand, I have noted in an earlier entry, that the business side of the Journal is in need of improvement.
I do not know if in the end, the Murdoch bid is the best chance for the long-run survival of what is good about the Journal. But I do wish the Journal, and the Journal‘s journalists, well.
(p. C1) On May 14, more than 100 reporters, editors and executives clustered in The Wall Street Journal’s main newsroom to mark the retirement of Peter R. Kann, the longtime leader of their corporate parent, Dow Jones & Company.
Mr. Kann, in rolled-up shirtsleeves, was typically self-effacing about his own contributions to the company. But the celebration of the past was muted by worry about The Journal’s future. A few weeks earlier, Rupert Murdoch’s News Corporation had offered $5 billion to buy Dow Jones. The Bancroft family, owners of a controlling stake in the company, rebuffed the offer at first, but there were signs that some of them were wavering.
Mr. Kann, who had been advising the family against selling, expressed hope that Mr. Murdoch would not prevail, using an image of The Journal as a citadel trying to repel an invasion by tabloid barbarians.
“The drawbridge is up,” Mr. Kann told the group. “So far, so good.”
For employees at Dow Jones, the 11 weeks since they learned of the Murdoch offer have been a wrenching time, raising the prospect of fundamental changes at an organization that had already had its fill of big changes in the last couple of years — with Mr. Kann being replaced by Richard F. Zannino as chief executive, with Marcus W. Brauchli taking over from Paul E. Steiger as top editor; and with a shift of its mission, by adding a Saturday paper and more lifestyle articles to appeal to new advertisers, and investing heavily in its digital properties.
. . .
(p. C12) The anti-Murdoch forces enjoyed one of their brief lifts on June 29 when The Journal reported that Leslie Hill, a Bancroft family member, had grave reservations about selling to Mr. Murdoch. Someone enlarged The Journal’s dot drawing of Ms. Hill, a retired airline pilot, adding the words “I Fly with Leslie” above her face. Copies of the makeshift poster appeared in Journal offices around the country.
. . .
As the chances of an alternative have appeared to wane, more reporters and editors have polished their résumés and approached rival publications about jobs. Some have even talked of starting their own business news Web site.
Many voiced disappointment in the Bancrofts, the family that has owned the company for more than a century and taken great pride in it, for not playing a leading role in running it for more than 70 years.
“We understand that for the Bancrofts this is a choice between getting much richer, and holding onto something because they believe in it,” a reporter said. “What they may not realize is that many of us in the newsroom have made the same choice. There are a lot of people here who could be traders or lawyers, people with M.B.A.’s, who could be making a lot more money. To us, this is not an abstract choice.”
For the full story, see:
 Rupert Murdoch. Note that the image is a tribute, or humorous small jab at, the hallmark image style of the Wall Street Journal, in which photographs are re-done by artists into an example of something like pointillism. (True also of the poster image above.) Source of the image: online version of the NYT article cited above.
Rupert Murdoch. Note that the image is a tribute, or humorous small jab at, the hallmark image style of the Wall Street Journal, in which photographs are re-done by artists into an example of something like pointillism. (True also of the poster image above.) Source of the image: online version of the NYT article cited above.


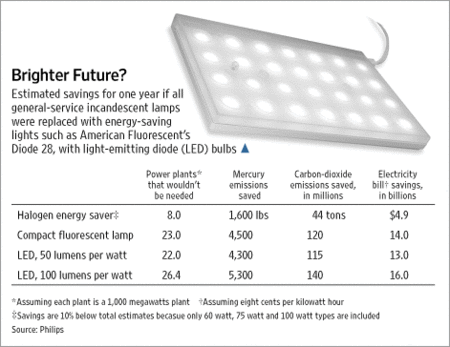
 The bulb I like, but don’t want to be forced to use. Source of image: online version of the WSJ article cited above.
The bulb I like, but don’t want to be forced to use. Source of image: online version of the WSJ article cited above.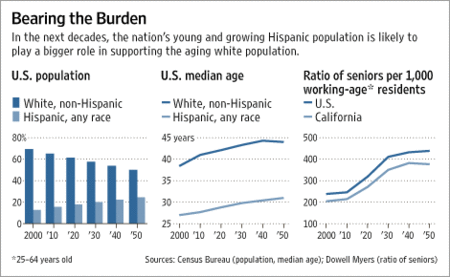
 Source of graphic: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below. 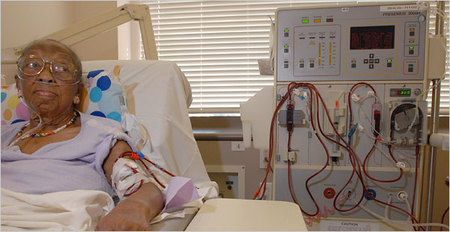
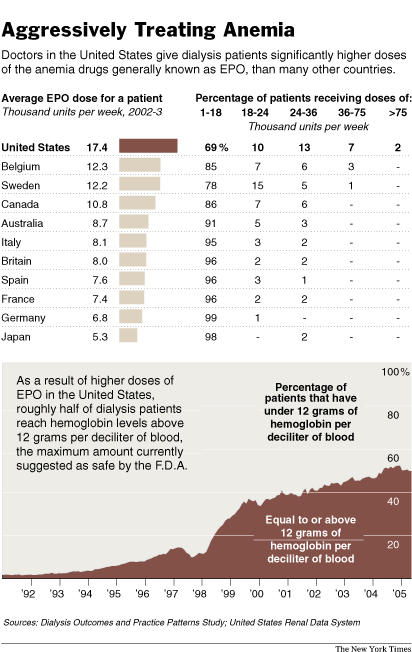
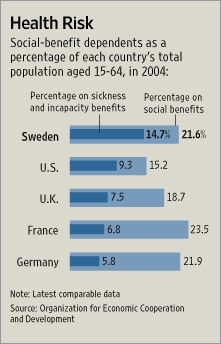 Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited below. A former Swedish teacher who had been receiving government disability payments for being allergic to electricity. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article cited above.
A former Swedish teacher who had been receiving government disability payments for being allergic to electricity. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article cited above.
 Source of the map: online version of the NYT article cited above.
Source of the map: online version of the NYT article cited above.