 Voters in line to vote for President in Senegal on 2/25/07. Source of photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
Voters in line to vote for President in Senegal on 2/25/07. Source of photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
My old Wabash professor Ben Rogge used to say that rulers liked to build pyramids to proclaim their glory. He mentioned the Egyptian pyramids, and he mentioned the whole government-created capital city of "Brasilia" in Brazil.
When rulers in a poor country invest a lot of tax money in infrastructure, such as roads, how much of that is due to their belief in mistaken economic theories, and how much to their wanting to build their own version of the pyramids?
In either case, at least it can be said that the people probably benefit more from their taxes being used to build roads, than from their taxes being used to build pyramids. At least the roads can be complementary to transporting goods, and to the mobility of labor.
But the people would benefit even more if they could keep the tax money to use for their own purposes.
(p. A3) DAKAR, Senegal, Feb. 25 — Moudou Gueye was confident that Senegal’s presidential election on Sunday would turn around his fortunes, at least in the short term.
Seven years ago he voted for Abdoulaye Wade, a rabble-rousing professor who, after decades in opposition to Socialist Party rule, sailed into office buoyed by the votes of frustrated young people like Mr. Gueye, who is now 32. They hoped that Mr. Wade, a free-market liberal, would transform this impoverished nation’s economy, which had been stunted by generations of ineffective central planning.
. . .
. . . Senegal has had relatively robust economic growth that has hovered at around 5 percent over several years (it was lower last year, owing in part to high fuel prices, according to government officials), compared with the 1 percent achieved during much of the Socialist era, and dozens of huge public works projects.
While in some ways the country is better off, economic growth and a building binge have not produced large numbers of jobs in a country struggling to make the transition from an agrarian society based largely on peanut farming to one that harnesses the wealth of a global economy.
. . .
Countering criticism that Mr. Wade is too old to serve another term — his official age is given as 80, but many people suspect he is older — his daughter, Sindiély, who has worked as a special assistant to the president, said he was as sharp and agile as ever.
“It is not a question of age,” Ms. Wade said as she waited to cast her vote in downtown Dakar. “It is a question of dynamism and ideas and what you have planned for your country.”
Along Dakar’s seaside roadway, young men marveled at the cars whizzing below a brand-new overpass, one of Mr. Wade’s long-anticipated public works projects.
Pap Ndiaye, an 18-year-old street vendor who sells baby clothes to people stalled in traffic, said the newly completed road was a sign that the country was moving in the right direction.
“Wade has done a lot for this country,” Mr. Ndiaye said. “Our hope is that he will stay and finish his work.”
Less than a mile away, the road abruptly ends with a bright yellow sign that says “déviation,” or detour. With a hard turn to the right, drivers pour off the broad new highway, and back into the tangled, chaotic streets of one of Dakar’s oldest and poorest neighborhoods.
For the full story, see:
(Note: ellipses added.)


 Molly McGrath. Soure of photo: online version of the Omaha World-Herald article cited below.
Molly McGrath. Soure of photo: online version of the Omaha World-Herald article cited below.

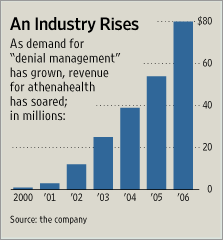 Source of graph: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
Source of graph: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
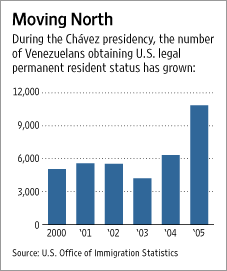 Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
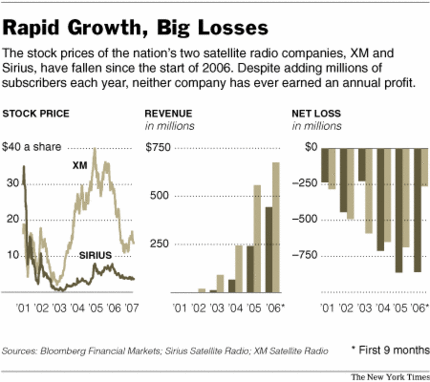
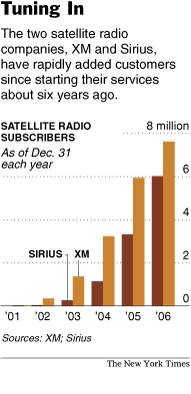
 Bush meets an actor playing the role of Washington at Mount Vernon on President’s Day. Source of photo: online version of the NYT article cited below.
Bush meets an actor playing the role of Washington at Mount Vernon on President’s Day. Source of photo: online version of the NYT article cited below.